Are you looking for innovative ways to make a positive change in the world while getting potential returns? Green bonds, which raised an incredible $257.7 billion globally in 2019 alone, could be your answer.
This blog post will guide you through the benefits and opportunities that these sustainability-focused financial tools offer. So let’s dive into the green revolution of investment!
Key takeaways
●Green bonds are like loans for projects that help the environment, such as clean energy and energy efficiency.
●They offer benefits for issuers, including access to sustainability-focused investors, lower interest rates, and potential tax incentives.
●The green bond has seen significant growth in recent years, with $257 billion raised globally in 2019 alone.
Understanding Green Bonds for Investment
Green Bonds are fixed-income debt instruments that raise capital for sustainability-focused projects such as energy efficiency and renewable energy.
They work by underwriting, certifying, and monitoring these projects to ensure the funds are used for their intended purpose.
The green bond market has experienced significant growth in recent years.

What are Green Bonds?
Green Bonds are like loans. People give money to groups who want to help the Earth. These groups will pay back this money with some extra overtime.
The extra money is seen as a thank-you for the loan.
Green Bond is used only for projects that help nature. This can include making clean energy, like from the sun and wind, or making buildings use less power.
For these bonds to work right, other firms must check them often. Green bonds come in short- or long-dated maturities and have various types of coupons and
This commitment to advancing the climate transition goes back to the first green bond, issued in 2007 by the European Investment Bank (EIB), the lending arm of the European Union (EU).
The funds raised by that five-year bond were earmarked for projects in renewable energy and energy efficiency, contributing to the EU’s climate change strategy.3
Since then, green bonds have become an approximately €1.5 trillion market.
Dominated in the early years by multilateral development banks such as the European Investment Bank (EIB) and the World Bank, which issued its first corporate green bond in 2008, the market has seen the range of green bond issuers expand to include companies and governments across the globe seeking investment to drive their plans to reduce greenhouse gas emissions (GHG) and guard against physical climate risks.
The investor base has also expanded to include a growing number of traditional fixed-income investors, not just those focused primarily on impact and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria.
How do Green Bonds work?
Green bonds are like other bonds but with a green plus point. They are loans for only green, clean, or earth-friendly projects.
A company or government can issue these bonds. The money from selling the bond must go to clean energy plans or other projects that help our Earth.
Firms who know a lot about these things check and say yes to the bond issue. They make sure the project does what it says it will do for our Earth.
Money people who want to do good as well as make money can buy these bonds.
This makes the Green Bond very popular for big, costly projects that help our Earth.
These include putting up wind farms, making buildings use less energy, and other works that cut harmful gas that heats our Earth.
Companies or governments pay back the loan from the bond over time with added interest to the money person who bought it.
The company or government tells how its project is doing in reports after the bond is issued.
This helps everyone see where their money goes and how it helps our Earth.
It also draws more eyes to the firm’s work for a cleaner, better world.

The growth of the green bond market
Green bonds are taking off all over the world. The green bond market has seen big growth since it started in 2007. In just 13 years, it grew about 95% each year on average.
By 2019, people bought $51.3 billion worth of green bonds in the U.S. alone.
The Green Bond Principles, published by the International Capital Market Association (ICMA) in 2014, contain project categories that are broad in scope, but they all contribute to environmental objectives such as climate change mitigation and adaptation, natural resources conservation, biodiversity conservation, and pollution prevention and control.
By setting out best-practice guidelines for issuers to promote greater transparency and accurate disclosure of key information, they have helped the market become more standardized, facilitating traceability and supporting the sustainable development goals of green bonds into a full-fledged segment of the fixed-income market.
This shows that more people and businesses want to invest in green projects.
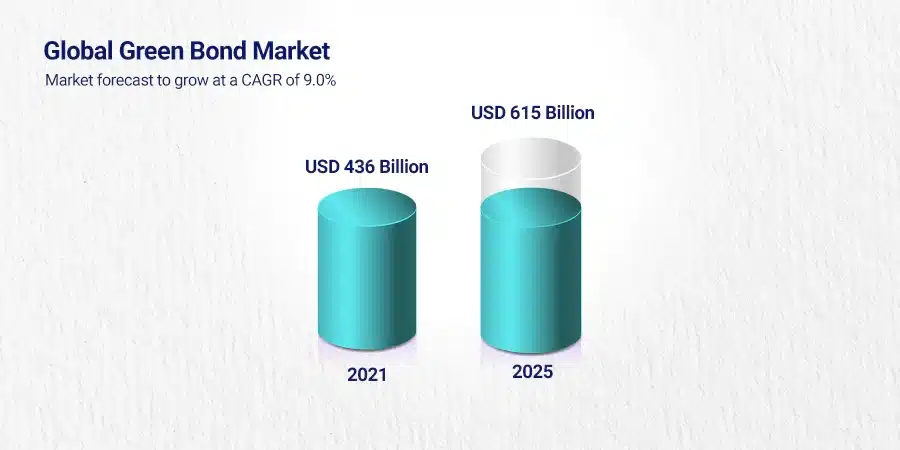
That’s why there was $257.7 billion worth of green bonds sold around the world that same year! The total value of all the green bonds from the start is now a huge amount — one trillion dollars!
This makes clear how much interest there is in putting money toward climate-friendly efforts.
It speaks volumes about what we can expect from future changes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Green Bonds
Green Bonds offer several advantages for issuers, including access to emerging markets of sustainability-focused investors and potential tax benefits and incentives.
However, they also come with their disadvantages, such as added transaction costs and the need for ongoing monitoring and reporting on environmental impacts.
Comparatively, Green Bond provides a more environmentally friendly investment option when compared to traditional bonds.

Benefits for issuers
Green bonds offer several benefits for issuers. Firstly, they can help increase visibility into a company’s green investments and demonstrate its commitment to sustainability.
This increased visibility can attract more investors who are interested in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investments.
Secondly, organizations with a strong credit rating can raise low-cost capital through green bond issuance. These bonds often have lower interest rates compared to traditional bonds due to their environmentally friendly nature.
Lastly, green bond issuers may also capture tax benefits and incentives depending on the jurisdiction they operate in. Overall, issuing green bonds can not only provide financial advantages but also enhance an issuer’s reputation as a sustainable and responsible organization.
Green Bonds versus traditional bonds
When comparing green bonds to traditional bonds, several key distinctions stand out. Green bonds are distinctively aimed at funding projects that contribute positively to the environment and are therefore categorized as a type of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) investment.
In contrast, traditional bonds are more generic and can be used to fund a wide range of projects, without any specific environmental or sustainability focus.
This comparative analysis between green bonds and traditional bonds highlights their unique features and benefits.
Criteria | Green Bonds | Traditional Bonds |
Purpose of Funds | Funds are exclusively used for sustainability-focused or environmentally friendly projects. | Funds can be used for any purpose, without any specific focus on sustainability or environmental impact. |
Structure | Shares have a similar structure to traditional bonds as they are both fixed-income and debt instruments. | Generally, a debt instrument offers a fixed-income instrument. |
Requirements | Projects funded by green bonds must adhere to certain sustainability requirements. | There are no specific sustainability requirements for projects funded by traditional bonds. |
Third-Party Involvement | Third-party firms are typically involved in underwriting, certifying, and monitoring green bond issuance. | Third-party involvement in underwriting, certifying, and monitoring is not mandatory. |
Investor Appeal | Green bonds are attractive for investors interested in ESG investments with a focus on sustainability. | Traditional bonds may not specifically attract ESG-focused investors. |
Tax Benefits and Incentives | May offer tax benefits and incentives. | May not offer the same tax benefits and incentives as green bonds. |
Investment Opportunities in Green Bonds
The investment opportunities in Green Bonds are promising due to the growing demand for sustainable investments and the potential for solid returns.
State of the Green Bond Market
Green bonds have experienced significant growth in recent years, indicating a strong and vibrant market. The green bond market reached $257 billion in 2019, demonstrating its potential for investment opportunities.
This growth can be attributed to various factors, such as increasing awareness of environmental issues and the desire for sustainable investments. Additionally, the demand for green bonds has been driven by both institutional investors and retail investors who are interested in combining financial returns with positive environmental impacts.
The state of the green bonds market is further bolstered by regulatory support and industry standards that promote transparency and credibility. For example, the Green Bond Principals (GBPs) provide guidelines on what qualifies as a green project, while organizations like the Climate Bonds Initiative and the International Capital Markets Association offer certification frameworks for verifying green bond issuances.
Furthermore, major players in finance have embraced the green bond market. Developmental banks, municipal entities, city governments, and commercial institutions like Goldman Sachs Renewable Power and PNC Financial Services Group have issued their own green bonds to fund sustainable projects.
Notable companies like Apple and Engie have also entered this space.

Requirements for issuing a Green Bond
To issue a Green Bond, organizations must meet certain requirements, including:
- The projects funded by the bond must have clear environmental benefits and contribute to sustainability goals.
- The issuer needs to establish a green bond framework that outlines the criteria for project selection and evaluation.
- The issuer must underwrite, certify, and monitor the bond issuance through third-party firms.
- The projects funded by the bond must align with recognized standards such as the Climate Bonds Standard or Green Bond Principals.
- Issuers may need to provide pre-issuance reports, second-party opinions, and post-issuance reports to ensure transparency and accountability.
- The issuer’s creditworthiness may be assessed through credit ratings or evaluations of their environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance.
- Issuers may benefit from tax incentives or other financial rewards for issuing green bonds.
- Organizations can issue green bonds in various formats like loans, revenue bonds, securitization bonds, or other debt instruments.
Outlook for Green Bonds
The outlook for green bonds is promising, as the market continues to grow and attract more investors. The demand for sustainable investments is increasing, and green bonds offer an opportunity to support projects that have a positive environmental impact while also generating financial returns.
Governments, corporations, and other issuers are recognizing the benefits of green bonds and are expected to continue issuing them in the future.
With billions of dollars already issued both domestically and internationally, it’s clear that there is a strong interest in financing projects related to renewable energy, energy efficiency, and other sustainability initiatives.
As more investors prioritize environmental considerations in their investment decisions, the market for green bonds is likely to expand further.
Conclusion
In conclusion, green bonds offer numerous benefits and investment opportunities. And providing investors a way for organizations to fund sustainability-focused projects while attracting investors interested in ESG investments.
With the growing market and potential tax incentive, green bonds are a promising avenue for capital-intensive projects with measurable sustainability impacts.
FAQs
The green bond is a financial instrument used to raise funds for projects that have positive environmental impacts, such as renewable energy or sustainable infrastructure. Investors buy these bonds, and the proceeds are then allocated to specific “green” projects.
Investing in a green bond allows individuals to support environmentally friendly projects while potentially earning a financial return. It also helps promote sustainability and contributes to global efforts to combat climate change.
Like any investment, there is some level of risk involved with the green bond. However, many investors consider them relatively safe because they are typically issued by reputable organizations or governments with strong credit ratings.
To invest in green bonds, you can contact your financial advisor or broker who can help you find suitable options based on your investment goals and risk tolerance. Alternatively, you may choose to invest through mutual funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) focused on green investments.









