Fixed Income Structured Products offer investors a unique way to diversify their portfolios and potentially enhance their returns.
But before delving into this investment avenue, it is crucial to understand the fundamentals.
Fixed Income Structured Products are financial instruments created by combining various fixed-income securities with derivative components.
These products are designed to meet specific investment objectives and provide tailored solutions for investors. They offer a way to customize risk and return profiles based on the investor’s preferences.
Summary
In this article, we will explore:
Fixed Income Structured Products are hybrid
investment instruments that combine fixed-income securities, such as bonds, with derivative components.
They are designed to provide risk and return characteristics that suit the investor’s needs.
There are several types of Fixed Income Structured Products available in the market. Some common examples include:
– Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs)
– Asset-Backed Securities (ABS)
– Mortgage-backed securities (MBS)
– Credit-Linked Notes (CLNs)
Fixed Income Structured Products offer several advantages, including:
– Enhanced yield potential
– Portfolio diversification
– Tailored risk and return profiles
– Exposure to specific sectors or assets
While Fixed Income Structured Products have their benefits, they also come with risks. It is important to be aware of factors such as:
– Credit risk
– Market and interest rate risk
– Complexity and lack of transparency
– Liquidity risk
When evaluating Fixed Income Structured Products, it is crucial to consider factors such as:
– The underlying asset and their creditworthiness
– Derivative components and their associated risks
– Cost structure and fees
– Potential returns and risks
Before investing in Fixed Income Structured Products, investors should carefully consider factors such as:
– Risk tolerance and investment objectives
– Understanding of the product structure and
associated risks
– Adequate diversification within the portfolio
– Review of the issuer’s creditworthiness
Fixed Income Structured Products are subject to regulatory oversight.
It is important for investors to understand the regulatory framework and ensure compliance to protect their interests.
Compliance with regulations such as disclosure requirements and suitability rules is crucial when dealing with these products.
By understanding Fixed Income Structured Products, their types, advantages, risks, evaluation factors, and regulatory framework, investors can make informed decisions and effectively incorporate these instruments into their initial investment strategy.
What are Fixed Income Structured Products?

Fixed Income Structured Products are specialized financial instruments that investors utilize to accomplish their desired investment goals. These products are designed to provide a unique blend of fixed-income returns and customized risk exposures.
The creation of these products involves pooling various fixed-income assets, such as mortgages, loans, or bonds, which are then divided into tranches with different levels of risk.
One of the key advantages of Fixed Income Structured Products is their ability to offer limited risk exposure. Investors can mitigate their risk by investing in
specific tranches that align with their risk tolerance.
For instance, an investor looking for lower-risk options may choose to invest in the most senior tranche, which has the first claim on the underlying assets and offers a lower yet more stable and positive return.
Moreover, these structured products provide investors with customized returns. Each tranche within the product offers distinct levels of returns. Senior tranches generally offer lower yields but provide greater capital protection.
On the other hand, junior tranches offer higher potential returns but come with increased risk. This allows investors to select the tranche that best suits their return expectations.
Structured products also enable investors to tailor their risk profiles. They offer exposure to specific risk factors such as interest rate risk or credit risk.
For example, an investor who anticipates an increase in interest rates can invest in a structured product focusing on interest rate-linked assets. This enables them to benefit from rising interest rates.
In addition, Fixed Income Structured Products promote diversification. By holding a diversified pool of underlying assets, these products reduce the concentration risk associated with investing in individual bonds or loans.
This diversification effectively spreads the risk across different asset classes, enhancing the overall risk/reward profile of the investment.
Lastly, structured products can be customized to meet specific investment horizons. Investors can choose products with varying maturities according to their desired investment timeframe.
Short-term investors may prefer products with a maturity of one to three years, while long-term investors may opt for products with a maturity of five to ten years.
- Enhanced yields
- Portfolio diversification
- Tailored risk and returns
- Exposure to specific assets
- Principal protection
- Complexity and opacity
- Credit risk
- Market and interest rate risk
- Liquidity risk
- Cost structure and fees
- Suitability concerns
Types of Fixed Income Structured Products
Explore the diverse world of fixed-income structured products and their various types. Discover the fascinating realm of Collateralized Debt Obligations, Asset-Backed Securities, Mortgage-Backed Securities, and Credit-Linked Notes.
Uncover the intricacies and opportunities that each of these types offers, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the possibilities within fixed-income structured products.
So, buckle up and get ready to dive into the realm of these financial instruments that can shape your investment journey.
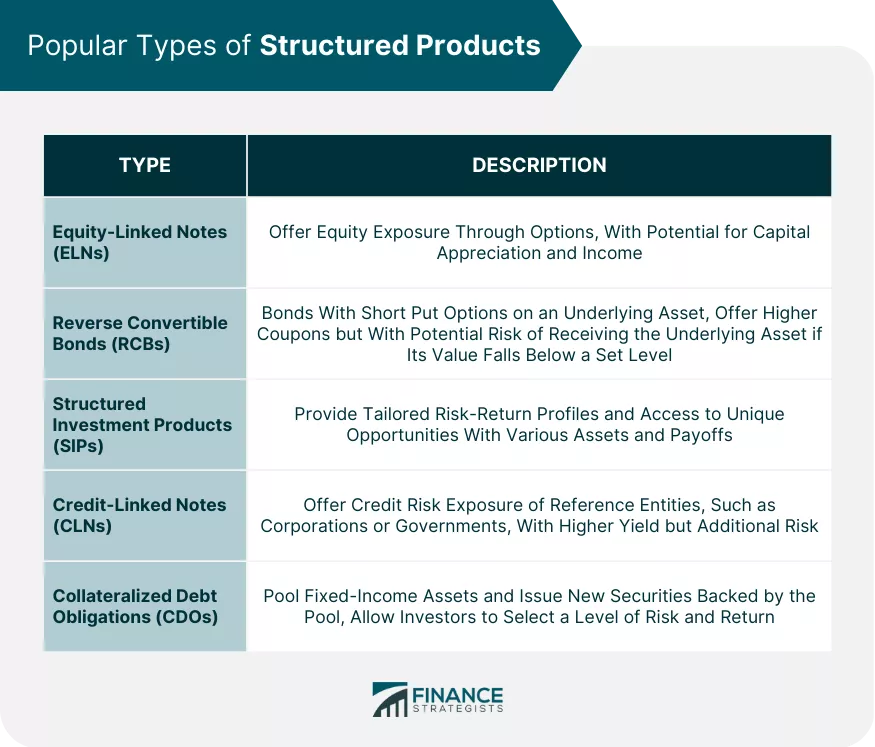
Collateralized Debt Obligations
strategies but are subject to stricter regulations to prevent another financial crisis.Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs) are a type of fixed-income structured product that combines various debt instruments into a single security.
These instruments are then divided into different tranches, each with varying levels of risk and return potential.
CDOs, also known as Collateralized Debt Obligations, are created by investment banks or financial institutions and are typically backed by a pool of assets such as corporate bonds, loans, mortgages, or even other CDOs.
Here are some key facts about Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs):
- Structure: CDOs are structured in a way that allows investors to potentially earn higher yields compared to investing in individual bonds or loans. The different tranches of a CDO have varying levels of risk and return potential, with the higher tranches being less risky but offering lower yields, and the lower tranches offering higher yields but with higher risk.
- Risk and Return: The risk and return profile of a CDO can vary depending on the quality of the underlying assets and the structure of the tranches. Higher-rated tranches, also known as Collateralized Debt Obligations, are considered safer investments as they have priority in receiving payments from the underlying assets, while lower-rated tranches are more exposed to potential default risk.
- Diversification: Collateralized Debt Obligations (CDOs) provide investors with the opportunity to diversify their portfolios by gaining exposure to a wide range of assets. This diversification can help reduce the overall risk of the investment.
- Credit Ratings: CDOs, including Collateralized Debt Obligations, are assigned credit ratings by rating agencies based on the quality of the underlying assets and the structure of the tranches. These ratings provide an indication of the creditworthiness and potential default risk of the CDO.
- Market Liquidity: The market for CDOs, including Collateralized Debt Obligations, can vary in terms of liquidity. During times of financial stress, the market for CDOs can become less liquid, making it difficult to buy or sell these securities at desired prices.
- Regulatory Considerations: After the global financial crisis of 2008, regulatory scrutiny of CDOs, including Collateralized Debt Obligations, increased significantly. Regulations such as the Dodd-Frank Act in the United States imposed stricter rules on CDOs to enhance transparency and reduce systemic risk.
Collateralized Debt Obligations gained prominence in the early 2000s, particularly in the mortgage market. However, during the global financial crisis of 2008, the weaknesses of these instruments became apparent.
The collapse of the housing market led to significant losses in CDOs backed by mortgage-backed securities, causing widespread financial turmoil.
This highlighted the risks associated with CDOs and led to increased regulatory oversight and a decline in their popularity.
Today, CDOs, including Collateralized Debt Obligations, continue to be used in certain investment

Asset-Backed Securities
Asset-backed securities, also known as ABS, are a type of fixed-income structured product that is backed by a pool of underlying assets. These assets can include loans, receivables, or other financial instruments.
The cash flows generated by the underlying assets are used to support the payments made to investors in the asset-backed securities. One advantage of asset-backed securities is the diversification they offer. By pooling together a variety of assets, the risk is spread across a larger portfolio.
This can help to reduce the impact of any individual asset defaulting. Asset-backed securities also provide investors with the opportunity to invest in specific asset classes that may not be easily accessible through another investment vehicle.
For example, investors can gain exposure to residential mortgages, commercial loans, or credit card receivables through asset-backed securities.
However, there are some risks and considerations to be aware of when investing in asset-backed securities. The credit quality of the underlying assets is important, as any defaults or delinquencies can impact the performance of the securities.
The structure of the security, such as the order of payment priority and the presence of credit enhancements, should also be carefully evaluated. When evaluating asset-backed securities, it is important to consider the quality of the underlying assets, the potential for cash flow variability, and the overall market conditions.
Investors should also take into account their risk tolerance and investment objectives before investing in these securities. Fact: Asset-backed securities played a significant role in the global financial crisis of 2008, as the collapse of the subprime mortgage market led to widespread defaults and losses in these securities.

Mortgage-Backed Securities
Mortgage-backed securities are a type of fixed-income structured product that is created by pooling together a group of mortgages and then selling interests in that pool to investors. These Mortgage-Backed Securities are backed by the cash flows generated from the underlying mortgage loans.
Investing in Mortgage-Backed Securities offers several advantages. Firstly, they provide investors with an opportunity to earn a steady stream of income.
This income is derived from the monthly mortgage payments made by homeowners, which are then passed on to the investors.
Secondly, Mortgage-Backed Securities are backed by a tangible asset – the underlying real estate properties – which can provide a certain level of security.
Lastly, these securities offer a level of diversification as they are usually backed by a pool of mortgages, spreading the risk across multiple borrowers.
However, there are also risks and considerations to be aware of when investing in Mortgage-Backed Securities.
One risk is prepayment risk. If interest rates decline, homeowners may choose to refinance their mortgages, resulting in the early repayment of the loan and a loss of future interest payments for the investor.
Additionally, Mortgage-Backed Securities are also exposed to the risk of default by borrowers, especially in times of economic downturn.
When evaluating Mortgage-Backed Securities, it is important to consider factors such as the creditworthiness of the borrowers, the loan-to-value ratios of the underlying properties, and the historical performance of similar securities.
It is also crucial to understand the structure of the security, including the tranches and the priority of cash flows.

Credit-Linked Notes
Credit-Linked Notes (CLNs) are a type of fixed-income structured product that offers investors exposure to credit risk by linking the performance of the note to the creditworthiness of an underlying reference entity. Here are some key points to consider when it comes to
- Structure: CLNs are structured instruments that combine a bond-like feature with a credit derivative. They are typically issued by financial institutions and provide investors with an opportunity to earn a yield that is higher than traditional bonds.
- Credit Risk: CLNs are designed to transfer credit risk from the issuer to the investor. The investor is exposed to the creditworthiness of the reference entity, which could be a corporation, a group of corporations, or even a sovereign entity. If the reference entity defaults on its obligations, the investor may suffer a loss.
- Income Potential: CLNs offer investors the potential for higher yields compared to traditional bonds. The yield is typically higher because of the credit risk associated with the reference entity. However, it is important to note that higher yields come with increased risk.
- Linked to Credit Events: The performance of CLNs is linked to specific credit events such as default, bankruptcy, or credit rating downgrades of the reference entity. Upon the occurrence of a credit event, the investor may receive a predetermined payment, which could be a fixed amount or a percentage of the notional value.
- Diversification: CLNs can provide investors with an opportunity to diversify their fixed-income portfolios. By investing in CLNs linked to different reference entities across various sectors or regions, investors can spread their credit risk and potentially enhance their risk-adjusted returns.
- Investor Eligibility: CLNs are typically sold to institutional investors or high-net-worth individuals who have a good understanding of credit risk and the ability to bear the potential losses associated with these products. Retail investors are generally not eligible to invest in CLNs.
When considering investing in CLNs, it is important to thoroughly understand the structure, credit risk, income potential, and diversification benefits.
Investors should carefully assess the creditworthiness of the reference entity and the terms and conditions of the CLN before making any investment decisions.

Advantages of Fixed Income Structured Products
The advantages of fixed-income structured products, such as stability, potential for higher returns, and diversification, are evident.
Fixed Income Structured Products: What You Need to Know
- Stability: One of the key advantages of fixed-income structured products is the stability they offer. With their fixed interest payments, these products provide a predictable income stream. Therefore, they are suitable for conservative investors who prioritize stability over higher returns.
Potential for higher - returns: Fixed-income structured products may not offer the same level of returns as riskier investments. However, they often provide better returns compared to traditional fixed-income instruments, like government bonds or savings accounts. These products are specifically designed to generate attractive yields, making them a favorable option for investors seeking moderate growth.
- Diversification: Investors can benefit from diversification by including fixed-income structured products in their portfolios. By investing in a variety of structured products with different underlying assets, investors can spread their risk and potentially mitigate the impact of any single investment’s performance. Diversification plays a vital role in protecting against losses and enhancing the potential for earning consistent returns.
Enhanced risk - management: Structured products are designed to manage and mitigate specific risks. For instance, some structured products have built-in protective barriers or downside protection mechanisms that limit potential losses for investors. By incorporating risk management features, structured products aim to provide a more controlled investment experience.
- Flexibility: Fixed-income structured products offer flexibility when it comes to maturity periods. Investors have the opportunity to select products with varying maturity dates, allowing them to align their investments with their financial goals and timeframes. This flexibility enables investors to tailor their investment strategy according to their specific needs and preferences.
It is crucial to note that investment decisions should be based on individual circumstances, risk tolerance, and investment goals.
Consulting with a financial advisor before investing in fixed-income structured products is advisable to ensure they align with one’s overall investment strategy.

Risks and Considerations of Fixed Income Structured Products
When considering fixed-income structured products, it is important to be aware of the risks and considerations involved. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Complexity: Fixed-income structured products can be highly complex and may involve intricate financial arrangements. It is crucial to fully understand the product’s features, terms, and conditions before investing.
- Risk of Capital Loss: Like any investment, fixed-income structured products carry the risk of capital loss. The value of these products can fluctuate based on market conditions and the creditworthiness of the issuer. Investors should carefully evaluate their risk tolerance and investment objectives.
- Market Risk: Fixed-income structured products are subject to market risk. Changes in interest rates, credit spreads, and economic conditions can impact the value and performance of these products.
- Liquidity Risk: Some fixed-income structured products may have limited liquidity, meaning they are not easily bought or sold in the secondary market. This lack of liquidity can make it challenging to exit the investment before maturity.
- Credit Risk: Investors should be aware of the creditworthiness of the issuer. If the issuer of the structured product defaults on its obligations, investors may face a loss of principal.
- Callable or Puttable Features: Some structured products may have callable or puttable features, allowing the issuer or investor to terminate the product before maturity. These features can introduce additional risks and considerations, such as reinvestment risk or early redemption fees.
- Fees and Expenses: Fixed-income structured products may have associated fees and expenses, such as management fees or brokerage fees. These costs should be carefully considered as they can impact net returns.
It is crucial to conduct thorough research and seek professional advice when considering fixed-income structured products. Understanding the risks and carefully assessing the product’s suitability for your investment goals and risk appetite is vital to making informed investment decisions.
Fact: According to a study by the Bank for International Settlements, the outstanding notional amount of structured products reached $4.7 trillion by the end of 2020.

How to Evaluate Fixed Income Structured Products
When evaluating fixed-income structured products, it’s important to consider various factors that can impact the performance and suitability of these investment options. Here are some key aspects to evaluate:
- Structure: Examine the structure of the product, including the underlying assets, repayment structure, and any associated derivatives. Understand how the product generates returns and its potential risks.
- Credit quality: Evaluate the creditworthiness of the issuer or underlying assets. Look for any credit ratings provided by reputable rating agencies and consider the default risk associated with the product.
- Yield: Calculate the yield or return offered by the structured product. Compare it with other fixed-income investments to determine its relative attractiveness. Be cautious of excessively high yields, as they may indicate higher risk.
- Liquidity: Assess the liquidity of the structured product. Determine whether there is an active secondary market for trading the product and consider the potential challenges in buying or selling the investment if needed.
- Terms and conditions: Review the terms and conditions of the product, including any fees or expenses associated with the investment. Understand the redemption terms, maturity date, and any early exit options.
- Risk-reward profile: Evaluate the risk-reward profile of the product. Consider the potential upside compared to the potential downside and assess whether the level of risk is acceptable given your investment goals and risk tolerance.
When evaluating fixed-income structured products, it’s important to conduct thorough research, seek professional advice, and carefully read all relevant documentation.
Consider consulting with a financial advisor or investment professional who can provide personalized recommendations based on your individual circumstances and investment objectives.
Investing in fixed-income structured products can be complex, and it’s crucial to fully understand the features, risks, and potential returns before making any investment decisions.
By carefully evaluating these products, you can make informed choices that align with your investment goals and risk appetite.

Key Factors to Consider Before Investing in Fixed Income Structured Products
When considering investing in fixed-income structured products, there are several key factors to consider before making a decision.
It is important to assess your risk tolerance, understand the product’s duration, evaluate the issuer’s credit rating, consider the yield offered, assess the liquidity, ensure transparency, understand the legal and regulatory considerations, and consider how the product fits into your overall investment portfolio.
Risk Profile: Before investing in any fixed-income structured product, it is important to assess your risk tolerance. These products can have varying levels of risk, and it is crucial to understand the potential for loss and determine if the risk aligns with your investment goals.
Duration: The duration of a fixed-income structured product is an important factor to consider. Duration measures the sensitivity of the product’s price to changes in interest rates. A longer duration implies greater price sensitivity, which may not be suitable for all investors.
Issuer Rating: The issuer’s credit rating plays a significant role in the risk associated with the product. A higher-rated issuer implies lower default risk, while a lower-rated issuer indicates higher default risk. Consider the issuer’s financial stability and creditworthiness before investing.
Yield: The yield of the structured product is an essential aspect to consider. It represents the return on investment and can vary depending on the specific structure and features of the product. Evaluate the yield offered and compare it to other investment options.
Liquidity: Liquidity refers to how easily the structured product can be bought or sold in the market. Assess the liquidity of the product and determine if it aligns with your investment preferences. Less liquid products may experience challenges in selling or buying at desired prices.
Transparency: Transparency is crucial when investing in fixed-income structured products. Ensure that the product’s terms and conditions are clear and well-defined. Transparency helps investors understand the risks, rewards, and potential returns associated with the investment.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations: Understand the legal and regulatory framework surrounding the structured product. Ensure that the product complies with all relevant laws and regulations. This will provide you with confidence in the integrity and legitimacy of the investment.
Diversification: Consider how the fixed-income structured product fits into your overall investment portfolio. Diversification can help spread risk and enhance potential returns. Evaluate if the product complements your existing investments and contributes to a well-balanced portfolio.
When considering investing in fixed-income structured products, thoroughly analyze these key factors to make an informed investment decision that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance.

Regulatory Framework and Compliance for Fixed Income Structured Products
When it comes to fixed-income structured products, understanding the regulatory framework and ensuring compliance is crucial.
Compliance with regulations helps protect investors and maintain the integrity of the financial market. Here are some key points to consider:
- Regulatory Framework: Compliance with the regulatory framework is essential for fixed-income structured products. Various regulatory bodies, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States and the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the United Kingdom, oversee these products. They establish guidelines and regulations to ensure fair and transparent markets.
- Compliance: Compliance with regulations is of utmost importance for issuers of fixed-income structured products. They must provide comprehensive and accurate disclosures to investors, including information about the product’s structure, risks, and potential returns. Investors should carefully review these disclosures before investing.
- Suitability: Financial advisors play a crucial role in compliance by recommending suitable fixed-income structured products to their clients. They must assess the client’s individual financial situation, risk tolerance, and investment objectives to determine if a product is suitable before making a recommendation.
- Market Manipulation: Market manipulation is strictly prohibited in the regulatory framework. Any attempts to manipulate prices, mislead investors, or engage in fraudulent activities can have severe penalties and legal consequences.
- Risk Management: Compliance also involves having robust risk management processes in place for issuers and investors. This includes assessing the creditworthiness of the issuer, monitoring market conditions, and understanding the potential risks associated with the structured product.
Compliance with the regulatory framework is essential to ensure the fair treatment of investors and maintain market integrity. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in reputational damage, legal repercussions, and financial losses.
Conclusion:
Fixed Income Structured Products offer investors a unique and diverse range of investment options that can complement their overall portfolio strategy than traditional investments.
These hybrid instruments combine fixed-income securities with derivative components, providing tailored solutions to meet specific investment objectives.
With the potential for enhanced yields, portfolio diversification, and exposure to specific sectors or assets, structured products have garnered attention from investors seeking customized risk and return profiles.
However, it is essential to approach these products with a clear understanding of their complexities and associated risks.
Factors such as credit risk, market and interest rate risk, lack of transparency, and liquidity risk should be carefully considered before investing.
Investors must also assess their risk tolerance, investment objectives, and the suitability of the product within their broader portfolio.
To navigate the landscape of Fixed Income Structured Products effectively, investors should conduct thorough research, seek professional advice, and adhere to the regulatory framework.
Compliance with regulations is essential to safeguard investors’ interests and maintain market integrity.
While structured products can offer attractive features, they may not be suitable for all investors due to their complexity and risk profile.
Careful evaluation, transparency, and a comprehensive understanding of the terms and conditions will empower investors to make informed decisions that align with their financial goals.
Incorporating Fixed Income Structured Products into an investment strategy requires prudence and a balanced approach.
By weighing the advantages and risks and adhering to best practices, investors can leverage these instruments to diversify their portfolios, potentially enhance returns, and work towards achieving their financial objectives.
Engaging with a financial advisor can prove invaluable in navigating the nuances of structured products and making well-informed investment choices tailored to individual circumstances.
In the dynamic world of finance, a strategic and informed approach to Fixed Income Structured Products will serve investors well in unlocking their potential benefits and contributing to a well-rounded investment journey.

Frequently Asked Questions
Fixed income structured products are retail investment options that combine traditional securities, such as bonds, with derivatives to meet specific investment objectives. These products offer market participation and access to alternative asset classes, and their returns are based on the performance of underlying assets.
Some fixed income structured products, known as principal protected notes (PPNs), offer full or partial return of principal at maturity, regardless of how the underlying assets perform. These products may have barriers and buffers that determine the level of protection, providing contingent or hard protection against potential principal loss.
While fixed-income structured products offer potential upside gain and access to alternative asset classes, they come with unique risks. These products have complex terms and their costs can be relatively high and difficult to determine. The guarantee of principal protection is only as good as the financial strength of the issuer, and if the issuer goes bankrupt, investors may recover little or none of their investment.
Fixed-income structured products may not be suitable for all investors, as they can be complex and may not be fully understood by lay investors. These products are primarily designed to be buy-and-hold investments, and their maturities can vary. Additionally, structured products often lack liquidity, and there is no guarantee of a secondary market.
FDIC insurance applies to certain fixed-income structured products that involve underlying certificates of deposit. However, it is important to note that FDIC protection applies only to the invested principal, and any excess amount is subject to the credit risk of the issuing investment bank. It is essential to consider the financial condition of the issuer before investing in these products.
Investors can access fixed-income structured products through financial institutions, such as Fidelity, which offer these products to retail investors. Investors can submit indications of interest during an order period, but it is important to note that submitting an indication of interest does not guarantee an allocation. Investors can also find structured products on the financial institution’s website or through a representative.









