Navigating through the investment world can be tricky and confusing. Did you know that structured notes, first introduced in the UK during the early 1990s, are financial innovations that have brought profound changes to how we invest? This article goes into depth about their history, capturing key milestones from around the globe and providing valuable insights into how these investment tools have evolved over time.
Ready to embark on a fascinating journey through finance history? Dive into this captivating tale of structured notes!
Key takeaways
● Structured notes mix parts of debt and other things. They were first made in Europe around the 1980s.
● How much money they make changes with the market. Big banks play a big role in selling them.
● Germany, China, and Canada hold a lot of these types of notes now.
● Different kinds exist like income, growth, and digital notes. Each has special features depending on what assets they tie to.
Definition of Structured Notes
Structured notes are a kind of investment option. They mix bonds and other tools to make a new thing to invest in. In easy words, structured notes act like an “IOU” from banks. The bank tells you how much money they will give back when the note ends or matures.
It can get more complex with what is called derivative instruments. These cause your returns to change as per some benchmark such as an equity index. Structured notes might have some safeguards but also have risks like credit risk and lack of liquidity.
Be sure you understand these before investing!
Historical Timeline of Structured Notes
Delve into the storied past of structured notes, tracing their prosperous rise in the 1980s and ’90s, through a period of evolution and expansion from 2003-2010, culminating with modern developments that have shaped the landscape from 2013 to today.

The 1980s and 1990s: The Rise of Structured Notes
In the 1980s and 1990s, structured notes started to become more popular with US investors. But high investor minimums (as high as $1 million) made them accessible to only the ultra-wealthy and institutional investors. Meanwhile, both financial advisors and investors lacked the knowledge and resources that would help these practical investments go mainstream. This was a new way for banks to bring people into the stock market. People were drawn by fresh ideas that meant payoffs could be based on different types of assets.
These structured notes had parts of debt securities and parts of derivates mixed in them. How well they did relied on how other things like products or money rates did too. During this time, many types of structured notes came out with special features like main amount protection and limits on top returns.
2003-2010: The Evolution and Expansion of Structured Notes
Big changes happened to structured notes from 2003 to 2010. Before this time, only rich people could buy these via private banks. But after, more people had access to them. Companies like Citigroup and Morgan Stanley started selling a lot of these notes too.
Still, it was not all good news during these years as issues came up in 2008. The market saw a drop due to fewer rules over the products by the SEC and FINRA. It pushed for tighter checks on how structured products work because of this fall in sales.
2013-2018: Modern Developments in Structured Notes
Big changes came to structured notes between 2013 and 2018. Markets in Germany and Switzerland became very strong. Spain and Italy, once leaders, fell back a bit. New laws made it harder to use strange payoffs or tools in these products.
But there were still challenges for the people who made these notes. Interest rates were very low during this time, which made it hard to attract people with the promise of big returns.
By now, many places in Europe had already been using structured products for a while, sold by banks and other groups alike!
Structured Notes Around the World
Delve into how countries like Germany, France, China, India, Canada, and Mexico have adopted structured notes as part of their financial landscape; discover the unique adaptations and regulations each region has implemented to cater to their dynamic market needs.
Continue reading for an intriguing global tour through the world of structured notes.
Germany and France: European Pioneers
Germany and France led the way in Europe with structured notes. They both became big players early on. Germany has a large market for these types of products. This makes it one of the biggest in all of Europe.
Sales in other places like the UK, Norway, and the Netherlands went down a lot after problems with credit. These countries have not bounced back yet. But Germany and Switzerland stepped up to become leaders.
Spain and Italy were leaders before but now they are not leading anymore.
Since 2009, laws have made things change a bit. Now complex payoffs and weird underlyings are less common in these kinds of products.
China and India: Asia's Adoption of Structured Notes
China and India are now using structured notes more. This change came with new rules set by the government. Also, banks now offer a larger number of these products. Their goal is to boost the offerings that are on record in their books.
Both countries saw this secondary market grow quickly due to these reasons.
Canada and Mexico: North America's Use of Structured Notes
Canada and Mexico are now using structured notes more. They link these to Constant Maturity Swap rates, also known as CMS rates. A CMS rate is part of how they set the coupon rate on many notes sold in Canada and Mexico.
These include steepeners or autocallable reverse convertible features which make them complex. Some retail investors have lost money because they didn’t fully grasp the strategy and risks.
Today a wider number of people can invest in these products that once were only for the very rich.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Structured Notes
This section delves into the various pros and cons of investing in structured notes, such as potential income and diversification benefits contrasted with possible risks like credit risk and lack of liquidity.
Benefits of Structured Notes
Structured notes can guard your money against risk. They let you join in the stock market fun without fear of losing all your cash. You can choose how safe to play it with these notes.
The profit (return) you make depends on how well the things, or assets, they are tied to do. For example, if a note is linked to a group of stocks and these stocks perform well, you will earn more money.
These instruments attract different types of investors now, not just those who have heaps of extra funds at hand.
Potential Risks and Drawbacks
Buying structured notes has some dangers. The main danger is credit risk. This means if the company that sold you the note fails, your money may be lost. Another risk comes from call features in these notes.
If a note leaves before it’s due, you might get less back than what you paid for it. You also might not get fair prices because some people don’t know enough about this kind of investment to set good prices for them — known as lack of liquidity and inaccurate pricing.
When rates go down far, selling these products becomes hard too. One more thing: even though they say “protected,” principal-protected notes do carry market risks! Be careful with them.
Types of Structured Notes
From income notes that offer regular payments to growth notes aimed at principle appreciation, and principal protected notes offering safeguard on the invested capital, structured notes come in various types including digital ones which payout based on a pre-determined event occurrence.

Income Notes
Income notes are a special kind of structured note. These notes tie to Constant Maturity Swap or CMS rates. Our income will change depending on these rates. Some common features are knock-in options, protection for our main money, and a cap on the highest returns.
Big banks like Citigroup, Morgan Stanley, and Goldman Sachs issue many of these income notes.
Growth Notes
Growth notes are a special kind of investment tool. Both debt and derivative pieces make up these notes. This mix helps to shape how growth notes work.
The most important part of the working of Growth Notes is the reference asset. The reference asset guides how well growth notes will do as investments. If this asset does well, then the growth note does too and investors get good returns on their money invested in these notes.
Sometimes, some added features might also exist in these kinds of structured notes like steepeners or autocallable reverse convertible features that can change how much return they give back to investors.
Also, it’s key to understand one thing about this type of structured note: every individual investor’s result with them may not be the same because what you gain from a growth note depends very strongly upon the performance of its referenced assets.
Principal Protected Notes
Principal Protected Notes are a kind of structured notes. They promise to keep the money you put in safe. These notes give back the starting cash when they end. This happens even if the markets go down or up! Yet, there is a risk still.
The bank that gives out these notes must be able to pay you back. You also might not make much extra money with these notes since your earnings usually have a set limit.
Digital Notes
Digital notes are a special kind of structured note. They mix debt and things called derivatives. You can think of digital notes like a cake with many layers. Some layers might protect your money, some might put a cap on how much you can make, and others decide how far into the game you can go.
But here is the cool part: these notes protect you from bad stuff happening in the market! The amount they guard against depends if it’s hard or soft protection. So that’s what makes digital notes unique in the world of structured notes.
Important Factors to Consider When Investing in Structured Notes
Insightfully exploring crucial parameters, this section navigates through the maturity of notes, underlying assets, return on investment, and protection levels, imperative for making informed decisions on investing in structured notes – immerse into the detailed exploration ahead.
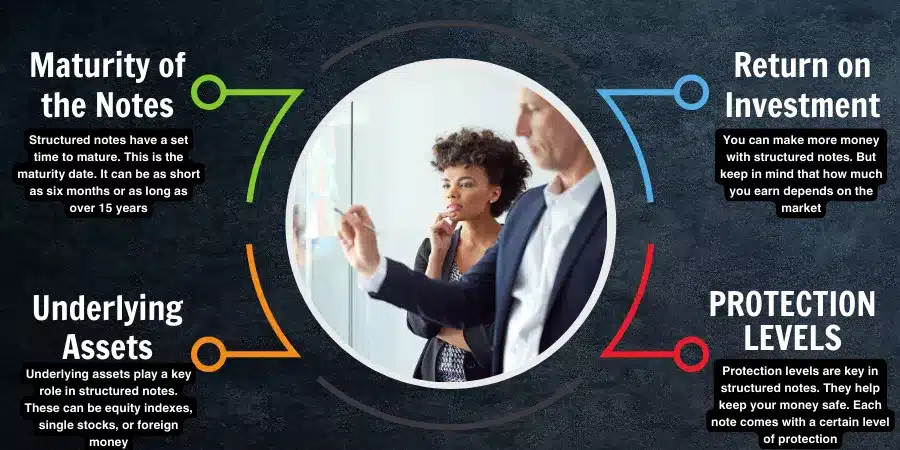

Maturity of the Notes
Structured notes have a set time to mature. This is the maturity date. It can be as short as six months or as long as over 15 years. The end of this time is when you get your money back.
This fixed period plays a big part in how much risk you take on with structured notes. Longer times mean there’s more chance for something to go wrong and make them less valuable. These longer periods also mean you cannot use your money during this time unless there are special terms that let you sell the note early.
Underlying Assets
Underlying assets play a key role in structured notes. These can be equity indexes, single stocks, or foreign money. The way an underlying asset performs decides how the structured note does too.
So, good performance by an underlying asset leads to good returns from the structured note. Also, many different features of a structure note depend on these assets such as knock-in aspects and rate of returns.
Return on Investment
You can make more money with structured notes. But keep in mind that how much you earn depends on the market. This is known as Return on Investment (ROI). If the market does well, your earnings will go up.
But if it does bad, your earnings may drop. So, always watch the market trends before putting money into structured notes. Also, know that low-interest rates and changes in law can cause a fall in profits from these types of investments.
Protection Levels
Protection levels are key in structured notes. They help keep your money safe. Each note comes with a certain level of protection. This is the least amount you can get back from your initial investment.
High levels mean more safety for your money. But low levels mean there’s more chance of losing it all if things go wrong with the assets of the notes. It’s important to know about these levels before putting your money into structured notes.
How do they work?
A structured note is basically a zero coupon bond tied to a derivatives package. These derivatives are usually in the form of call-and-put options that can hedge against market volatility.
The majority of the investor’s principal is invested in a zero coupon bond issued by the bank or the financial institutions. When the bond matures, the principal plus interest is returned to the investor. Meanwhile, the remaining amount invested in the derivatives package provides enhanced returns and principal protection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, structured notes have evolved significantly since their inception in the 1980s, offering a unique blend of investment opportunities. While they provide potential benefits such as capital protection and market participation, investors must be aware of the associated risks, including credit risk and liquidity challenges. These notes have gained popularity worldwide, with different regions adopting them and adapting to local market needs. To make informed decisions, investors should carefully consider factors such as maturity, underlying assets, potential returns, and protection levels. Regulatory improvements aim to enhance investor safeguards in this complex investment strategy.
FAQs
Structured investment products are types of investments that banks make. They link to other assets like interest rates or foreign currencies.
The Global Financial Crisis hurt many people with a high net worth who spent money on exotic underlying and faced losses due to the credit crisis.
Yes, when Lehman Brothers fell about 13 years ago, it shook up markets all around the world and led to new rules for these kinds of investments.
Asia Pacific Market as well as European countries like Austria, Belgium, and Finland have seen a rise in its use over time.
Investment banks warn even those with an understanding of Investing Basics: There may be pay-off structure differences that put your savings at risk or unexpected tax implications causing extra payments aside from federal taxes!
Nowadays US Securities And Exchange Commission (SEC) needs every single note sold to have clear information on fees & costs as well as Creditworthiness; it helps protect investors against losses.









