Do you ever wonder how banks manage risks and enhance their profitability? Why Do Banks Issue Structured Notes?
They use something called structured notes, a type of investment option lesser known in the U.S. but popular in Europe and Asia.
In this post, we’ll unravel the reasons why banks issue these financial instruments, helping you understand their potential role in diversifying portfolios and securing a positive return.
Ready to demystify structured notes? Exciting insights await!
Key takeaways
●Banks issue structured notes as a risk management tool to control losses during market downturns and diversify their investments.
●Structured products can enhance the profitability of banks by generating additional revenue through fees and taking advantage of market volatility.
●Customer demand is a key driver for the issuance of structured notes, with investors attracted to their flexibility, protection, and potential for higher returns.
Why Do Banks Issue Structured Notes
Structured notes are complex financial instruments issued by banks, offering investors a return based on changes in financial markets.
With defined risk characteristics and payout structures, these notes can vary greatly in complexity and transparency.
Often seen as an alternative to traditional debt offerings or direct equity investments, structured notes blend the features of bonds with an additional derivative and bond component linked to market performance.
Investors seeking flexibility may find a structured note appealing due to their customizable nature.
As opposed to fixed-rate returns from conventional bonds or equities, structured note payouts are often tied to the performance of the underlying asset such as stock indices, mutual funds, commodities, interest rates, or foreign exchange rates.
This offers a way for investors looking for yield enhancement or downside protection in uncertain markets.
Structured notes: why do banks issue them?
Banks issue structured notes for risk management, increased profitability, and customer demand.

Risk Management
Banks use structured notes as an essential tool in risk management. Since this financial instrument comes with in-built downside protection, they help control losses during market downturns.
This means even when the stock market plunges, note’s issuing investment bank remains relatively safe.
Risk management also involves diversifying investments to balance out any potential damages.
Structured notes may provide this flexibility by offering various payout structures and defined risk characteristics.
By issuing these notes, banks can smartly hedge against market risks while reducing overall portfolio volatility.
Increased Profitability
Banks or financial institutions find structured notes an enticing method for boosting profitability. Selling this financial instrument allows them to pocket hefty fees, enhancing their bottom line.
The flexibility of structured notes design means they can adjust the fee structure based on the underlying asset or market risk involved.
In some cases, investment banks may leverage the customer’s lack of knowledge about these complex financial products to impose higher costs, further increasing their profit margins.
Such profits become more promising in times of economic turbulence when traditional investing methods like bonds and equity investments yield lower returns.
Through many structured notes, banks effectively capitalize on market volatility to drive revenues upwards.
Customer Demand
Customers play a crucial role in driving the demand for structured notes. With the potential for defined risk characteristics and attractive payout structures, customers are attracted to these investment options.
In Europe and Asia, where structured notes have gained popularity, retail investors have embraced them as a way to diversify their portfolios while seeking downside protection.
Although lesser known in the United States due to limited access and high investment minimums, customer demand is growing as more individuals become aware of the benefits these products offer.
By understanding customer preferences and aligning their offerings with market needs, investment banks can meet this demand and provide customers with tailored solutions that address their investment goals and risk appetite.
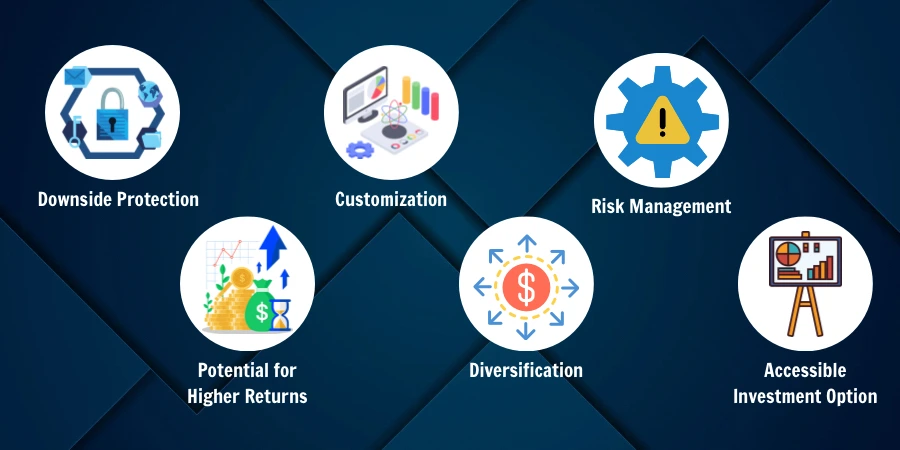
Benefits and Considerations of Structured Notes
The structured note offers several benefits and considerations for investors to take into account:
- Downside Protection: A structured note provides a level of principal protection against market downturns. Depending on the terms of the note, investors may be able to limit their losses or have a buffer against significant declines.
- Potential for Higher Returns: While structured notes offer downside protection, they also provide an opportunity for higher returns compared to traditional fixed-income investment. The payout structure of these notes can be designed to allow participation in market gains.
- Customization: The structured note can be tailored to meet specific investment goals and risk tolerance levels. Investors have the ability to customize features such as the underlying asset classes, return, and principal protection levels, and maturity date.
- Diversification: By incorporating structured notes into their portfolios, investors can diversify their holdings beyond traditional stocks and bonds. This can help spread risk and potentially enhance overall investment portfolio performance.
- Risk Management: The structured note enables investors to hedge against specific risks or volatility in the market. Through the use of options strategies, these notes can provide a way to mitigate risk and lower portfolio volatility.
- Accessible Investment Option: In some regions, structured products are available as retail products, making them accessible to individual investors with smaller investment amounts.
Debunking Common Misconceptions about Structured Notes
Structured notes are often misunderstood, leading to common misconceptions about their nature and suitability as an investment option.
Contrary to popular belief, the structured note can be relatively conservative in nature, offering defined risk characteristics that make them suitable for a range of investors.
Additionally, these notes provide flexibility in terms of payout structure, allowing investors to tailor the product according to their specific needs.
One misconception is that the structured note is only accessible to institutional investors or the ultra-wealthy.
While this may have been true in the past for U.S. markets, there has been a shift towards making a structured note more widely available to retail investors.
This means that everyday individuals now have the opportunity to benefit from this initial investment option.
Another common myth is that structured note is always hyper-aggressive and high-risk investments.
In reality, these products can be designed with downside protection features such as buffers or floors, which limit losses during market downturns while still allowing participation in potential upside gains.
This combination of principal protection and yield enhancement makes structured notes an attractive choice for many investors looking for a balanced approach.
Overall, it’s important not to underestimate the benefits and potential of a structured note due to misconceptions surrounding their complexity or risk level.
By gaining a better understanding of how these products work and considering them under the guidance of an experienced financial advisor or financial planner, investors can unlock new opportunities for portfolio diversification and potentially enhance returns without assuming excessive risk.
Potential investors are encouraged to consult with professional tax, legal, and financial advisors before making any investment into a Masterworks offering.
Conclusion
In conclusion, banks provide structured notes for several reasons. Firstly, they use them as a risk management tool to hedge against volatility in the investment market.
Secondly, a particular structured note can enhance the profitability of banks by generating additional revenue streams.
Lastly, customer demand plays a significant role in the issuance of these products, with investors seeking flexible and customized investment options that provide both downside protection and potential upside participation.
Overall, structured notes may offer a unique combination of features that make them an attractive choice for both banks and investors alike and to create better financial health.
FAQs
Structured notes are financial instruments offered by financial institutions that combine a fixed-income component with derivatives to create customized investment products.
Banks provide structured notes as a way to attract investors and generate revenue. These products offer investors the opportunity for potentially higher returns compared to traditional fixed-income investments, while also allowing banks to earn fees and profits from selling and structuring these complex securities.
Investing in structured notes can provide diversification, the potential for enhanced returns, and customization options tailored to an investor’s tolerance to risk and investment objectives. Additionally, some structured notes may offer downside protection features that limit losses if certain conditions are met.
Yes, investing involves risk. These include credit risk (the risk of default by the structured note issuer), market risk (fluctuations in underlying assets or indices), liquidity risk (difficulty to buy and sell structured notes), and complexity risk (understanding how the note works). It is important for investors to carefully consider these risks before investing and consult with a financial advisor if needed.








