The DTI ratio indicates how many more times your debt is in relation to your total gross income. For example, a DTI of five means your debt is five times your total gross income.
It’s a comparison between your monthly debt payments and monthly gross income. Money lenders use this financial metric to assess your borrowing risk.
When you file for an auto, mortgage, or other type of loan, lenders and banks use this ratio to evaluate how much of your income will suffice for your current debt obligations. It also determines how much more you are able to take on.
Calculating your debt ratio also helps choose the budgeting techniques to optimize your overall financial health.
This article explains what is a debt to income ratio, how lenders use debt to income ratio, what is ideal debt-to-income ratio, and more.
What is a Debt to Income Ratio?
A debt-to-income-ratio is a financial metric used by lenders to measure your ability to manage the monthly payments to pay off the money you want to borrow.
Like understanding your credit score, learning about your debt ratio is a crucial step to improve your overall financial stability. According to the 2024 Wells Fargo Money Study, over 40% of Americans struggle to get out of debt.
Understanding your DTI ratio can be helpful to make effective debt management strategies and apply for new credit.
Calculating your DTI ratio helps you to evaluate your comfort level with your current debt. Moreover, you can decide if borrowing more funds can be a wise choice. When you apply for a loan, lenders determine your DTI ratio to assess the risk of approving your credit request.
What is a Good Debt-to-Income Ratio?
The lower your ratio, the better. The ideal highest DTI varies from lender to lender and by product. For example, a back-end DTI of 35% or less usually shows that you are comfortable with your current debt payments. And you also have enough money leftover for daily spending and other financial goals.
That said, you may still qualify for a loan with a high DTI ratio of 50% or less. Some lenders may get ready to accept a more than 50% income ratio, but fees and interest rates may get high if you get approval.
How to Lower Your DTI Ratio before Applying for a Mortgage?
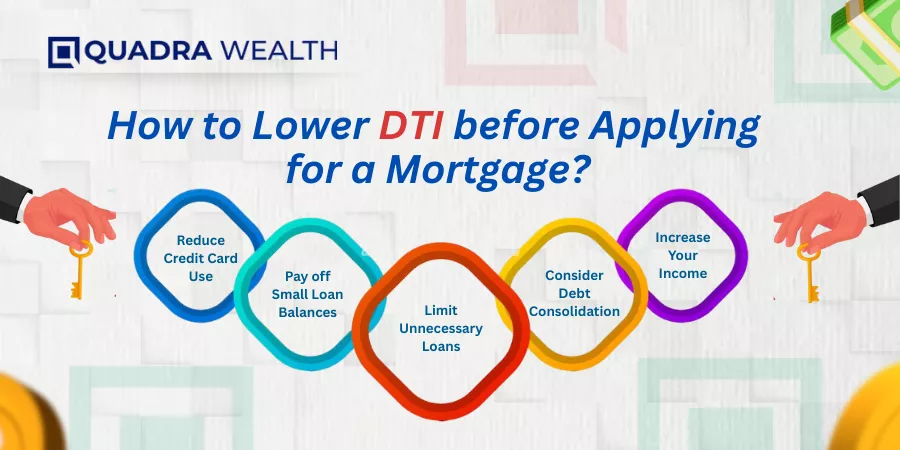
A lower DTI ratio can improve your chances of getting more loan. Whether you are looking to better your financial situation or simply want to apply for a loan, here are a few easy ways to lower your DTI:
Reduce Credit Card Use
Credit cards are a form of revolving credit. Your monthly payments may still appear on your credit reports even if you pay off your debt in full each month. A good credit score can help managing your debt. Make a plan to pay your credit card balances and reduce usage for a month or two before applying for a credit to reduce your DTI.
Pay off Smallest Debt First
If you have a loan with a relatively low remaining balance, you can use some of your savings to pay your debt faster and it can help reduce your DTI. If you are planning to apply for a conventional mortgage loan, lenders will generally omit a loan payment from your debt ratio if you have remaining payments of 10 months or fewer. And you may qualify for the next smallest debt.
Limit Unnecessary Loans
Try to avoid much debt unless it’s indispensable. If taking on new debt is absolutely necessary, try to take as little as possible to keep your monthly payments low. Your considerable income goes toward paying debts, so more loans can affect your credit score.
Consider Debt Consolidation
If you have to pay a lot of high-interest debt, consider debt consolidation. It would enable you to consolidate multiple payments into one, streamlining your debt payment process. Debt consolidation will lower your monthly payment in the meantime. It may also lower your debt-to-income ratio.
Increase Your Money You Earn Each Month
Consider starting a side gig to generate more income and ensure a balance between debt and income. There can be several options like requesting overtime hours, asking for a raise, moving to a higher-paying position, taking on a side hustle or getting a second job.
Why Debt-to-Income Ratio Matters?
The percentage of your DTI can impact your mortgage qualifications and credit eligibility. It can also have implications on your general financial well-being.
More specifically, here are some factors that explain why is debt-to-income ratio important.
Lenders Use Your DTI Ratio to Assess Your Loan Eligibility
Lenders consider your DTI along with other parameters like your credit score, income, credit history, and other factors, to decide whether to approve your loan application. Your better DTI ratio and your ability to repay decides your loan terms and the amount of loan.
A higher DTI leads to higher fees and interest rates and may even result in rejection of your application to borrow money. So, it’s critical to keep your DTI low to handle more debt.
It Can Affect Which Loans You Can Get
Creditors commonly have certain policies for the maximum DTI they’ll approve. For example, if your DTI is in the mid to upper 40% range, you can still qualify to obtain an auto loan, a credit card, a personal loan, or a student loan.
Moreover, some mortgage lenders may be prepared to work with you. However, mortgage lenders with lower debt to income limits may disapprove your application. And if your debt to income ratio is above 50%, your borrowing options may considerably be reduced.
Recurring Debt Can Affect Other Financial Goals
The more debt you have to pay, the more monthly income goes to paying debts. And you have the less spendable income you will have to allocate to your housing costs, retirement plan, emergency fund, or other financial goals.
For instance, if you use 50% of your income for debt payments, it may be challenging for you to keep up with your obligations. Consider finding ways to lower your debt.
Limitations of Debt-to-Income Ratio

Although important, the DTI ratio is not the only factor in credit decisions. A borrower’s credit score and credit history also impact loan approval decisions. A high debt-to-income ratio indicates the lower chances of approval. So, maintain your good DTI if you are inclined to take on more debt.
A credit score indicates how much you are capable of paying off your debts. This numeric value depends on information from your credit report, covering your balances relative to their credit limits, the number of open credit accounts, payment history, and any negative remarks like delinquencies.
The DTI ratio does not differentiate between different types of debt and the cost of servicing that debt. For example, credit cards typically have higher interest rates than student loans, but they are combined in the DTI ratio calculation.
If you shifted funds from your high-interest cards to one with a lower rate, your monthly payments will reduce. As a consequence, your DTI ratio and total monthly debt payments will drop. But your total debt outstanding would remain the same.
Debt-to-Income Ratio Guidelines
The maximum DTI ratio differs from lender to lender. Generally speaking, 43% is the highest debt ratio with which a loan seeker can still be eligible for a mortgage. Ideally, creditors prefer a DTI ratio lower than 36%, with no more than 28% to 35% of that debt allocated to mortgage payment.
Wells Fargo is a leading lender in the United States. The bank offers banking and lending products that consist of mortgages and credit cards to consumers.
Below is a rundown of its DTI ratio guidelines:
- 35% or below is generally considered favorable, and you can qualify for getting a loan. Possibly, you’ll have money leftover for paying monthly bills.
- 36% to 49% means your debt ratio is acceptable, but you have room for improvement. Creditors may require to meet other lending criteria.
- 50% or above ratio implies you have low funds to save or spend. Consequently, you won’t have much of your monthly income for an unexpected event, limiting your borrowing options.
The Bottom Line
The debt-to-income ratio is the percentage of your monthly gross income (your income before taxes and other deductions are taken out) that will be used to pay off your regular debt payments. Lenders determine your borrowing risk using your DTI ratio.
A DTI of 43 % is normally the highest ratio that a loan recipient can have and still be eligible for a mortgage. However, lenders typically look for ratios of no more than 36%. A low DTI represents enough money compared to debt servicing, and it makes a debt seeker more attractive.
It was all about what is a debt to income ratio, why it matters, and how it can help you achieve financial stability.
If you are looking for personal finance tips, Quadrawealth can offer you important insights and guidelines. Get in touch with us today!
FAQs
Q1. What is the Formula to Calculate a Debt-to-Income Ratio?
A: The formula includes dividing your total recurring monthly debt by your gross monthly income (income before taking out taxes and other expenses).
Q2. How Does a Debt-to-Income Ratio Impact an Individual’s Eligibility to Obtain a Loan?
A: A low debt ratio shows a good balance between income and debt, making you a more attractive candidate for loans. Creditors determine your borrowing risk by evaluating your DTI ratio along with your overall debt, income, and credit rating.
Q3. What Does Your DTI Ratio Exclude?
A: Debt in your DTI ratio doesn’t include expenses like utility bills and retirement contributions, and income doesn’t include one-time payments and unverifiable cash sources.






