Introduction
Corporate Bonds are bonds that help you leverage your investment portfolios in a safe manner.
These are debt securities that are issued by companies to raise their capital. Here, the firm raises its capital funds through public subscriptions.
As an investor, when you purchase corporate bonds, you get regular interest payouts until the tenor period or the maturity period of the investment.
You get a 100% return of your capital investment upon the completion of your maturity period.
On this parlance, let us discover ‘What Are Corporate Bonds?’ comprehensively:
What are the main features of Corporate Bonds?
These are the main features of Corporate Bonds. Let us have a rundown of pointers that correspond to the same:
Meaning and conceptualization
Companies that start afresh need working capital and fixed capital to run their operations. You must procure machinery and furniture, lease or buy property premises, and deal with many other assets you manage. These expenses refer to one-time expenses and, therefore, are treated as capital assets in the ledger books of accounts.
However, working capital requirements refer to money that is utilized to run the premises in a hassle-free manner. You must procure raw materials to manufacture finished goods. You must hire staff and pay salaries to them month on month. You must pay rental money to your landlord or commercial property owner. These expenses are recurring in nature and, therefore, contribute to the working capital requirements of the enterprise.
Here, to accommodate both fixed capital and working capital requirements, the firms issue debentures and corporate bonds and try procuring the money through public subscriptions. They pay interest on the capital provided and redeem these bonds upon the completion of a long-term tenure period comprising 10/15/ 20 years.
This is how corporate bonds are issued and circulated via financial corporations, banks, and other third-party intermediaries to public subscribers.
Who are the issuers?
Public corporation and Private Corporation firms issue corporate bonds by diving their capital requirements in denominations of $1000/ $2000.
Affordable denominations are worked at so that more and more subscribers can buy these corporate bonds from the firms.
Thousands of these bonds are circulated to the general public via public sector banks and privately owned financial corporations to allow companies meet their capital and working requirements.
Issued at Face Value or at Par Values
The Bond values are usually issued at face values and are usually redeemed at par values upon the end of the tenor period of maturity period that these bonds are backed with.
Say for instance, if the value of a corporate bond is $1000 per bond, then the investor redeems $1000 per bond, at the time this bond matures.
Here, the investor purchases the bond at $1000 per bond and redeems it at the same value.
Under an investment parlance, you conclude that the bonds are issued at a face value and are redeemed at the same par value at the time of redemption.
Coupon earnings for the investor
As the bonds are purchased at face value and redeemed at par values, meaning the purchase prices and redemption values measure the same, investors are provided coupon payouts as the return on investment for investing in these bonds. The coupons are paid quarterly, semi-annually, or annually.
Fixed coupon payouts
The coupons are usually fixed. It is the rate of interest that gets fixed by product issuing firms on each of these corporate bonds. The segregated payouts are disbursed to the investors on a quarterly, halfyearly or annual basis indeed.
Determining the creditworthiness of product-issuing firms
The credit ratings or individual credit worthiness of corporate firms are guaged by regulation authorities such as the S&P, the Moody’s or the CRISIL. Only if the credit ratings of the firms are good, the corporate bonds would be distributed for public subscription. This is done to protect the principal investment of retail and commercial investors on the whole.
Callable features may or may not be embedded on bonds
Principal Protection Notes or other Capital safe bonds come to you with a pre-set callable feature. Here, the product issuers can initiate a call feature to redeem the investments prior to their maturity periods.
Bonds can also have fixed-tenor horizons wherein the bonds stay redeemed only if the term of maturity gets completed on these bonds.
What are the benefits of Corporate Bonds?
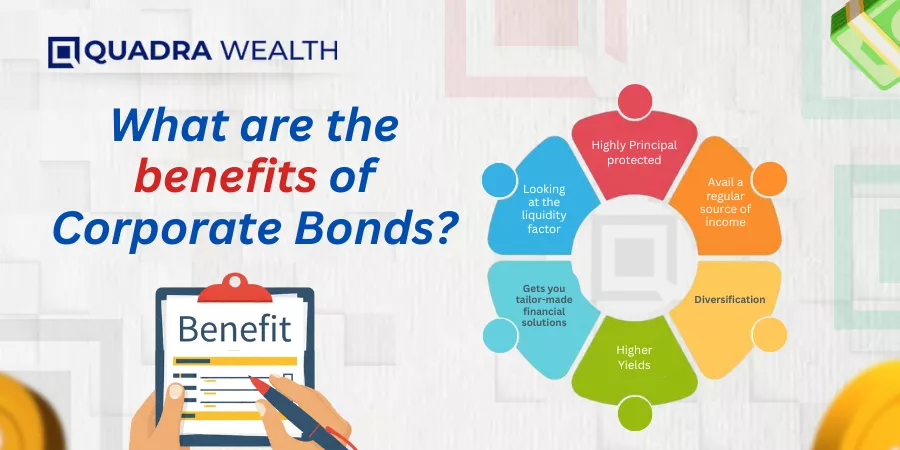
These are the benefits of Corporate Bonds. Let us have a rundown of pointers that are associated with the same:
Highly Principal protected
Bonds are principal protected capital investments that guarantee the investors with a 100% return of their principal or capital money irrespective of underlying market scenarios. Therefore, bonds are highly protected investment options that appeal to traditional investors, retirees and pensioners.
Avail a regular source of income
As an investor, you can avail a regular source of income. The bond issuers offer you coupon payouts quarterly, half-yearly, or annually. These are interest earnings distributed to you in the form of coupons.
The coupon-payment doubles up as a passive source of income over your regular earnings via your full-time jobs or business profits.
Diversification
Corporate bonds help you diversify your income portfolios in a streamlined manner indeed.
As an investor, you may have deposited your funds into heavy duty equities or variable interest paying portfolios. The market risks over losing your principal protection is higher with market-volatile financial instruments.
On the other hand, corporate bonds are entirely safe and secure as you are guaranteed the entire value of investment once you hold the bonds until the maturity period of these bonds. This way, you balance your portfolios to a greater extent indeed.
Higher Yields
Corporate bonds yield better returns over fixed-income securities or government-backed mortgage bonds. This is because the principal amount of investors is invested in high-paying financial assets that can garner attractive rates of return for the investors. Therefore, you can get attractive rates of returns when you have a basket of high-paying corporate bonds that belong to different enterprises and entities on the whole.
Gets you tailor-made financial solutions
Corporate bonds via different enterprises or entities help you gain a border perspective on how amalgamations, mergers and acquisitions (M&A) and private equity managing firms operate under volatile market scenarios.
This way, you can get tailored financial solutions based on the investment objectives you have in mind.
As a seasoned investor, you can invest via high-paying and capital-safe corporate bonds to fulfill the short-term, medium-term, and long-term financial obligations you have in mind.
Looking at the liquidity factor
Bonds can easily be sold in liquid markets like financial corporations or public sector undertakings or via secondary markets. Therefore, the bonds are highly liquid and flexible sources of investments that can amplify your investment portfolios on a considerable scale.
What are the risk factors of Corporate Bonds?

These are the risk factors of Corporate bonds. Let us have a rundown of pointers that are connected with the same:
Credit Issuing Risk
The investors may lose their principal investment and capital earnings if the product-issuing firm signs up for insolvency or bankruptcy. This is a risk factor that is pertinent to all types of investment options. However, government entities or authorities provide compensation to investors if the credit issuing company defaults on capital-protected investment portfolios.
Interest rate risk
When the interest rate of financial products increase, then the bonds fall in their values. This can pose a risk to investors who are heavily dependant on attractive investment earning portfolios for their survival.
For instance, retired officers, pensioners, and senior citizens rely upon capital-protected investments to raise their bread and butter toast on the table as these earnings are their life-long savings, and they do not have any other sources of income to bank upon.
Market risks
Unprecedented economic downturns like an outbreak of a global pandemic or declaration of recession does have a bearing on the value of principal protected capital bonds. In these scenarios, the investors may receive the partial value of their investments and not the whole portion of it.
Inflation risk
Corporate bonds provide fixed coupon payouts in the name of interest earnings. These earnings can be eroded in no time if the economies show increasing inflationary trends. Here the prices of goods and services turn dearer for consumers and the coupons may not add much of a value here.
Liquidity risk
The corporate bonds, when sold before their maturity periods, might incur significant losses in their values. Here, you may have to sell the bonds at distress sale values, losing a considerable portion of your capital wallet.
The Bottom Line
Capital-protected bonds offer immense value and, therefore, provide a leveraged degree of customization to investors on the whole. You must read the offer documents carefully before investing. What are your thoughts on this? Do let us know in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions or FAQs
Define Government bonds
Answer: Government bonds are debt securities that are offered by government companies or public sector undertakings like banks or government-funded financial corporations. The bonds are issued at par-value denominations to investors, and these offer fixed interest payouts to retail or traditional investors via coupon-backed interest payments.
Do mutual fund companies invest in bond funds or contribute to the bond market?
Answer: Yes, Mutual funds comprise of capital safe equities and bonds from different companies and enterprises. They buy corporate bonds from issuing companies and circulate them amongst investors over a fee. Higher interest bonds are typically included as basket earning portfolios.
Do you have rating agencies that provide bond ratings similar to stock exchanges?
Answer: Yes, you have rating agencies that differentiate junk bonds or junk investments from value-added bonds or investment securities. Credit ratings are accorded to bonds based on how capital safe they are and how they can enhance the investment portfolios of different types of investors.
What is your understanding of the term ‘coupon rate ‘?
Answer: Coupon rate refers to rate of interest that is designated by product issuance firms on bonds or fixed income securities. Here, corporate bonds are debt securities that offer higher interest rates or high-yield coupon rates as compared to government-backed bonds. While issuing the bonds amongst subscribers, they are further categorized as long-term bonds or short tenor bonds. The dividends earned on securities or bond prices differ based on the tenor of the investment plan.
What are the lucrative benefits a bondholder has?
Answer: Corporate bonds are capital-protected investment options, and the bonds may fetch interest payouts once every six months or so. The investment holder gets a greater level of principal protection and a low-risk investment option. Here, despite greater risk market volatilities, the bonds offer longer-term protection against the capital investment of investors. Govt-owned etfs or Fitch securities may also offer an enhanced participation rate of growing asset values as you invest in corporate bonds, treasury bonds, or other high-value securities.






