Deciding how to fund your business can feel like navigating a financial maze. Investing in a venture requires understanding the distinct differences between equity and debt financing options.
This article will empower you with knowledge about their pros, cons, and key character traits so you can make an informed decision best tailored to your business needs. Ready for some clear-cut advice? Let’s dive into the details of these two pivotal forms of financing!
Key takeaways
● Debt financing involves borrowing money that must be repaid with interest, while
equity financing involves selling a portion of ownership in return for capital.
● With debt financing, businesses retain control and ownership but have repayment
obligations and potential risks associated with failure to repay the loan.
● Equity financing provides extra working capital without repayment obligations but
requires sharing control and profits with investors.
● Businesses should consider factors such as repayment terms, ownership
implications, security concerns, and risk factors when deciding between equity and debt financing.
Understanding Debt Financing
Debt financing refers to the practice of raising capital for a business by borrowing money, which must be repaid with interest within a specified period of time

Definition of Debt Financing
Debt financing means getting money for your business by taking a loan. The loan must be paid back with interest over time. It is like borrowing from a bank or any other place that can lend you money.
You use this money to run your business, buy things you need, or pay people who work for you. The main thing about debt financing is that you have to give the money back after some time with some extra money known as interest.
But while paying it back, you still own your business fully without sharing it with anyone else.
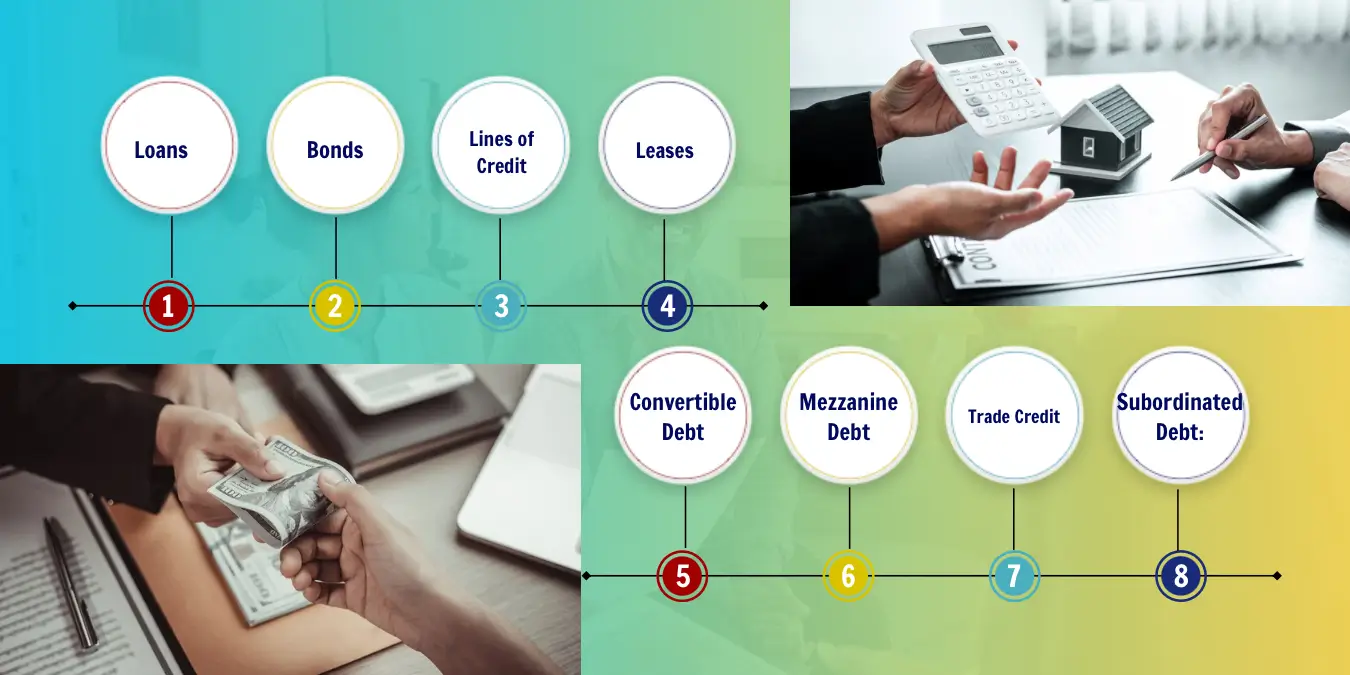
Types of Debt Financing
Debt financing has different types. The first type is term loans. This allows a business to borrow money and pay it back over time with interest.
Another type is business lines of credit. This can give a company flexible access to cash whenever they need it. Invoice factoring is another kind of debt financing. Companies use this by selling their invoices for cash upfront.
Business credit cards are used often too. They allow businesses to make purchases and pay the balance off later. Lastly, there are peer-to-peer lending services and SBA loans available for companies in need of funds.
Pros and Cons of Debt Financing
Debt financing, as a funding strategy, has various pros and cons that businesses must consider. These include the necessity for repayment, tax benefits, and the financial risk associated with failure to repay the loan.
- Full Control and Ownership: Businesses retain ownership and control when they opt for debt financing. They are not required to share profits or the decision-making process with investors.
- Tax-Deductible: Interest payments on the borrowed amount are tax-deductible. This aspect can lower the overall cost of the loan, making debt financing a potentially cost-effective option for businesses.
- Credit Building: Timely repayment of debt can help businesses build a strong credit history. This can be beneficial for securing future financing.
- Clear Repayment Plan: Debt financing comes with a clear repayment schedule. This can help businesses plan their budgets effectively.
- Repayment Obligation: Regardless of the business's profits or losses, debt must be repaid. This obligation can create financial stress, particularly during challenging economic times.
- Collateral Requirement: Most debt financing requires collateral. If a business fails to repay the debt, it could lose the assets put up as collateral.
- Higher Interest Costs: Depending on the terms of the loan, businesses might end up paying a significant amount in interest over time. This can increase the overall cost of the financing.
- Risk of Overborrowing: There is the risk of borrowing more than the business can afford to repay, which can lead to financial difficulties or even bankruptcy.
Understanding Equity Financing
Equity financing refers to raising funds for a business by selling shares of ownership in the company, allowing investors to become shareholders and participate in the profits and growth of the business.

Definition of Equity Financing
Equity financing is a way to get money for your business. You sell parts of your company, known as equity, to investors. In return, you get the funds needed for things like growth and expansion.
The investors also become part owners. They can weigh in on big decisions about the company’s future. Since this does not involve borrowing, no repayments are required. But it does mean sharing profits with all investors who hold equity in the business.
Types of Equity Financing
Equity financing comes in various forms. Each type can suit different needs, goals, and
stages of a business.
1. Angel Investors: These are wealthy people who provide money for a company. In
return, they want a piece of the business.
2. Venture Capital Firms: These firms give money to companies that are starting or
growing. They expect to get part of the company in return.
3. Crowdfunding Platforms: These online sites let many people put small amounts of
money into a company. This can add up to a lot.
4. Corporate Investors: Some big companies invest in smaller ones. They also want a
piece of the small company in return.
5. Initial Public Offering (IPO): This is when a company sells parts of itself to the public
for the first time.
Pros and Cons of Equity Financing
Equity financing is an alternative funding option that involves selling shares of your company to raise capital. This approach has its unique pros and cons.
- Provides extra working capital that does not have to be repaid, freeing up cash flow for business operations.
- Allows for the possibility of obtaining large amounts of funds, depending on the value and potential of your business.
- Gives the company access to the investors’ knowledge, contacts, and credibility, potentially leading to new opportunities and partnerships.
- No repayment obligations, making it a less risky option if the business fails.
- Requires giving up a portion of your company’s ownership, which means sharing control and profits with investors.
- Often involves a longer and more complicated process than debt financing, as it involves negotiating with potential investors and complying with regulatory requirements.
- Profit sharing means that investors will receive a portion of the company’s profits permanently, as long as they hold shares.
- Investors have a say in business decisions, which could lead to disagreements and conflict.
Comparing and Contrasting Equity and Debt Financing
Repayment terms, ownership implications, security concerns, and risk factors – understanding the key differences between equity and debt financing is crucial for your business’s financial success.
Don’t miss out on this essential information!

Repayment Terms
You pay back debt financing with set terms. These terms say how much money you need to pay and when you have to pay it. The payment often includes the loan amount and any interest charges.
If you do not make these payments, your business could be at risk. For example, if you used an asset as collateral for a business loan and fail to meet repayment obligations, the lender may take this asset.
Equity financing doesn’t have such repayments or risks because investors get their return from dividends or selling their share in the company’s profits.
Ownership Implications
Equity financing has important ownership implications for businesses. When a company chooses equity financing, it means that they are selling a portion of their ownership to investors.
This means that the investors become shareholders and have a say in the decision-making process of the business. They also share in the profits generated by the company. On the other hand, debt financing does not involve giving up ownership.
Businesses can borrow money from lenders and repay it over time with interest, but they maintain control over their operations and decision-making processes. However, it is essential to note that debt financing may come with certain restrictions that limit the activities and opportunities of a company.
It’s important for businesses to weigh these ownership implications when considering which type of financing is best suited for their needs.
Key facts:
– Equity financing involves selling a portion of ownership.
– Debt financing allows companies to borrow money without giving up control.
Security Concerns
Security concerns are an important factor to consider when choosing between equity and debt financing for your business. With debt financing, there is a risk of defaulting on loan payments, which can result in penalties and even asset seizure if collateral was provided.
On the other hand, with equity financing, you have to share ownership and decision-making power with investors, which may impact your control over the business.
It’s crucial to carefully assess these security concerns before making a decision about how to finance your business growth.

Risk Factors
Businesses must consider various risk factors when choosing between equity and debt financing. With debt financing, there is a risk of not being able to make timely loan payments, which can lead to financial strain and potential default.
Additionally, the interest charges associated with debt can create a heavy financial burden on the business. On the other hand, equity financing involves the risk of giving up ownership and sharing profits with investors.
This can result in a loss of control over important business decisions. It’s important for businesses to carefully evaluate their tolerance for risk and consider how it aligns with their long-term goals before deciding between equity and debt financing options.
Practical Examples: Debt vs. Equity Financing
Companies often face the decision of whether to use debt financing or equity financing. Let’s look at some practical examples to understand the differences between these two options.
In one scenario, a small business owner decides to expand their operations. They approach a bank for a business loan, which is an example of debt financing. The bank provides them with the requested funds and outlines the repayment terms, including interest charges.
Over time, the business owner pays back the loan in regular installments until it is fully repaid.
On the other hand, let’s consider another scenario where a startup company seeks equity financing. They pitch their business idea to venture capitalists who are interested in investing.
In exchange for capital, these investors become shareholders in the company and share ownership responsibilities and risks with the founder.
These two examples highlight key differences between debt and equity financing. Debt financing involves borrowing money that needs to be paid back with interest over time. It allows businesses to obtain immediate funds while being obligated to make periodic repayments.
Equity financing involves selling shares of ownership in return for capital without any repayment obligation but diluting control over decisions made by shareholders.
Understanding these practical examples can help businesses make informed decisions about which type of financing best suits their goals and circumstances.
How to Choose Between Debt and Equity Financing for Your Business
● Consider your business goals and growth plans
● Analyze your tolerance for risk
● Evaluate the repayment obligations of debt financing
● Assess the ownership implications of equity financing
● Research the interest rates and terms offered by lenders
● Explore the potential for investor influence with equity financing
That’s it! Remember, prioritize clarity and simplicity in your writing.

Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the key differences between equity and debt financing is essential for business owners. Debt financing allows companies to borrow money with repayments and interest charges, while equity financing involves selling a portion of ownership in return for capital.
Each option has its pros and cons, so it’s crucial to consider factors such as repayment obligations, ownership implications, security concerns, and risk factors when making financial decisions for your business.
Consider your goals, risk tolerance, and legal aspects before choosing the most suitable option for your needs.
FAQs
Equity financing involves selling shares of a company to investors, while debt financing involves borrowing money that needs to be repaid with interest.
The choice between equity and debt financing depends on factors like your business’s financial situation, growth plans, and risk tolerance. It’s best to consult with a financial advisor to determine the most suitable option for your specific needs.
Equity financing allows you to raise funds without incurring debt obligations or making regular repayments. Additionally, investors may bring expertise and connections along with their investment.
Debt financing does not dilute ownership control as it involves borrowing funds that need to be repaid, whereas equity financing involves selling shares which can result in a loss of ownership control as new shareholders come onboard.










