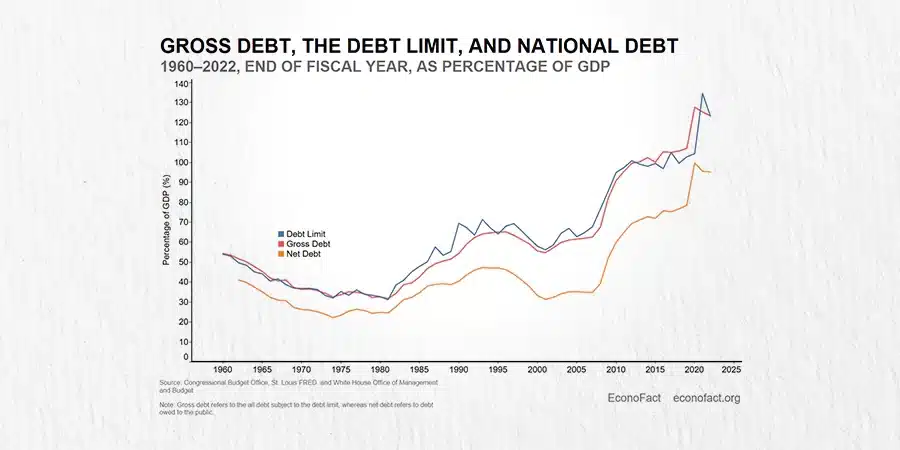
Debt ceiling what it means, often referred to as the ceiling debt, is a critical component of financial management and government spending.
Understanding the concept of ceiling debt is key to comprehending its implications on your finances and the overall economy. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the debt ceiling and its significance for your financial well-being.
Debt ceiling represents the maximum amount of money that a government can legally borrow to finance its operations and meet its financial obligations. It serves as a legal limit set by the government to control its borrowing activities.
Unlike other types of debt, such as national debt or personal debt, the debt ceiling specifically pertains to the borrowing cap established by the government.
The importance of the debt ceiling lies in its direct impact on the economy. When the government approaches or reaches the debt ceiling, it raises concerns about the government’s ability to fulfill its financial commitments.
This, in turn, can lead to serious consequences such as a potential default on debts, downgrading of credit ratings, increased borrowing costs, and a loss of investor confidence.
The effects of ceiling debt on your finances can be significant. It can indirectly impact interest rates as the uncertainty surrounding the government’s ability to manage its debt may increase borrowing costs for both individuals and businesses.
Ceiling debt can affect the government’s spending decisions, potentially leading to budget cuts or reduced funding in certain areas.
Managing ceiling debt requires proactive measures to avoid reaching the borrowing limit.
This can involve implementing fiscal policies that promote responsible spending, reducing budget deficits, and finding alternative sources of revenue.
Potential solutions to manage ceiling debt include increasing the debt ceiling, implementing spending reforms, and fostering economic growth to generate additional income.
The implications of ceiling debt extend beyond individual finances, affecting financial markets as well.
The uncertainty surrounding the debt ceiling can lead to market volatility, impacting stock prices, interest rates, and overall investor confidence.
Furthermore, the long-term effects of ceiling debt can include inflationary pressures, reduced economic growth, and limitations on future federal spending.
Debt Ceiling What It Means ?
Ceiling debt, also known as the maximum amount of debt that a government or organization is legally allowed to accumulate, is a crucial aspect of financial stability.
It is determined by a limit set by lawmakers or financial institutions to ensure responsible fiscal decisions and prevent excessive indebtedness.
One real-life example of ceiling debt is seen in the United States.
The U.S. Congress sets a limit on government borrowing to finance operations. When the debt nears the ceiling, Congress must address the situation by either raising the limit or reducing spending to manage the debt effectively.
Understanding what ceiling debt entails is of great importance for individuals and policymakers. It enables informed discussions on fiscal policies, federal spending, and overall financial stability.
By being aware of the limits and consequences associated with ceiling debt, individuals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the economic landscape and make well-informed financial decisions.
Neglecting to address ceiling debt can lead to credit rating downgrades, increased borrowing costs, and a negative impact on the economy.
How is Ceiling Debt Different from Other Types of Debt?
Ceiling debt distinguishes itself from other forms of debt in various ways. It specifically pertains to the maximum amount of debt that a government can accumulate, as prescribed by legislation to restrict government borrowing.
Unlike personal or corporate debt, ceiling debt is intricately tied to the functioning of the government. Reaching the debt ceiling can have detrimental effects, such as potential default, which can adversely impact the economy by reducing investor confidence, increasing borrowing costs, and potentially leading to a credit rating downgrade.
Furthermore, ceiling debt can also influence the federal government, necessitating the prioritization of expenditures and potentially resulting in reductions to vital services and programs.
Having an understanding of these distinctions is crucial in comprehending the ramifications of ceiling debt on the economy and personal finances.

Why is Ceiling Debt Important?
Ceiling debt is important for several reasons. Why is ceiling debt important? It sets a limit on the amount of debt that a country or organization can accumulate, ensuring fiscal responsibility.
It also affects the credit rating of a nation or entity. If the ceiling is consistently raised, it may lead to a downgrade in credit, increasing borrowing costs.
Additionally, ceiling debt impacts investor confidence. When investors see that a country is reaching its debt ceiling, they may become concerned about its ability to repay loans.
Finally, ceiling debt has implications for spending and budgeting. When a country reaches its government debt limit, it must either cut spending or raise revenue to avoid defaulting on its obligations.
This can have significant consequences for public debt services and economic stability. Understanding why ceiling debt is important is crucial for maintaining fiscal discipline and ensuring the long-term financial health of a nation or organization.

How Does Ceiling Debt Impact the Economy?
Ceiling debt impacts the economy by creating uncertainty and disrupting global financial markets. When the government reaches the ceiling debt, it cannot borrow more money and must rely on available government funds.
This can cause delayed payments to sectors like government employees, contractors, and beneficiaries of government programs. Understanding Ceiling Debt: What It Means for Your Finances
The impact on the economy is multi-fold. First, it can decrease consumer and investor confidence. Uncertainty about the government’s ability to fulfill financial obligations may lead to reduced spending and investments, slowing economic growth.
Second, it can increase government borrowing costs. To manage the ceiling debt, the Treasury securities department may take extraordinary measures like suspending certain types of debt issuance or using certain government funds from other government accounts.
These measures can result in higher interest rates as investors demand higher returns for increased risk. Third, ceiling debt can lead to a downgrade in the country’s credit rating.
Rating agencies assess the government’s ability to manage debt and repeated or uncertain ceiling debt can call into question the country’s creditworthiness. This may result in higher borrowing costs for the government and private sector.
What Are the Consequences of Reaching the Ceiling Debt?
Reaching the ceiling debt has significant consequences on the economy and financial markets. It can lead to a loss of confidence in the government’s ability to manage finances, resulting in higher borrowing costs for the government.
This can cause a government shutdown, halting non-essential services and potentially furloughing employees, which negatively impacts the economy by reducing consumer spending and slowing down growth.
Reaching the ceiling debt can also lead to a downgrade of the government’s credit rating, making it more difficult and expensive to borrow money in the future.
It is important to address the issue promptly, as failure to do so can have long-term consequences for the economy, financial markets, and the government’s ability to fund essential programs and services.
Policymakers must take measures to manage and avoid reaching the ceiling of the debt limit to maintain financial stability and safeguard the economy.

Does Ceiling Debt Impact Borrowing Power?
Does ceiling debt impact borrowing power? Ceiling debt impacts borrowing power. When the government reaches its debt limit, it has borrowed the maximum allowed by law, limiting its ability to borrow more money. This affects the government’s borrowing power.
When the government can’t borrow more money, it faces challenges meeting financial obligations, such as paying employees or fulfilling commitments.
It also causes delays or disruptions in federal government services and programs. It hampers the government’s response to unforeseen circumstances or emergencies requiring additional funding.
Reaching the government debt limit has negative implications for the economy. It increases uncertainty and undermines investor confidence, leading to higher borrowing costs for the government, businesses, and individuals.
Economic growth slows down, and investment and job creation are hindered. To avoid reaching the debt limit, governments must responsibly manage their federal debt.
This includes implementing effective fiscal policies, controlling spending, and exploring ways to increase revenues without relying solely on borrowing.
By doing so, governments can maintain their borrowing power and ensure the stability and growth of their economies.
What Happens to Government Spending During Ceiling Debt?
During ceiling debt, spending by the government can be impacted in several ways. First, if the debt ceiling is reached and the government cannot borrow more money, non-essential services may be suspended or payments to government contractors and suppliers may be delayed.
This can significantly affect spending because essential services still need to be provided, but non-essential programs and projects may be put on hold.
Secondly, during ceiling debt, the government may implement spending cuts to manage the debt and avoid breaching the debt limit.
This can result in reduced funding for various government programs and initiatives, affecting both the public and private sectors.
Thirdly, the uncertainty and potential instability caused by ceiling debt can also impact on spending. To manage the situation and protect the economy, the government may choose to be more cautious with spending and implement tighter fiscal policies.
This can lead to reduced government spending overall.
Managing Ceiling Debt
Managing ceiling debt is crucial for financial stability and minimizing stress. When it comes to managing your ceiling debt, there are several effective strategies that you can incorporate:
- Create a budget: Take the time to assess your income and expenses thoroughly. This will help you determine how much you can allocate towards debt repayment each month.
- Prioritize debts: To save money in the long run, it’s important to focus on paying off the debts with the highest interest rates first.
- Reduce expenses: Cutting unnecessary spending is an excellent way to free up some funds that can be used to pay off your debt. Understanding Ceiling Debt: What It Means for Your Finances
- Consider debt consolidation: If you have multiple debts, consolidating them into one loan with a lower interest rate can simplify debt management.
- Negotiate with creditors: Reach out to your creditors and discuss the possibility of lower interest rates or more manageable payment plans. It’s worth exploring these options to make your debt more manageable.
- Seek professional help if needed: If you find yourself struggling to manage your debt, don’t hesitate to consult a financial advisor or credit counseling agency. They can provide valuable guidance and assistance.
- Avoid new debt: While you work towards paying off your existing debt, it’s important to resist the temptation of taking on additional debt.
8. Monitor your progress: Keep a close eye on, prioritize debt payments, and celebrate milestones along the way. This will help you stay motivated and continue managing your ceiling debt effectively.
By incorporating these strategies into your financial plan, you can take control of your debt and work towards achieving financial stability.

What Measures Can Be Taken to Avoid Reaching Ceiling Debt?
In order to avoid reaching ceiling debt, certain measures can be taken to ensure financial stability. One crucial step is to increase revenue by implementing policies that spur economic growth.
This can be achieved by reducing taxes for businesses and individuals, attracting foreign investments, and promoting exports.
Additionally, cutting spending is another essential measure. It is important to carefully analyze budgets and identify areas where expenses can be reduced.
This may involve eliminating unnecessary expenditures, streamlining government operations, and eliminating redundancies.

To effectively manage resources, it is crucial to prioritize essential programs and services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
By allocating funding to these priority areas and reducing funding for less critical areas, a more focused approach can be achieved.
Implementing fiscal responsibility measures is also key. This can be accomplished by adopting strict budgetary controls, implementing transparency measures to prevent corruption and mismanagement of funds, and establishing mechanisms for accountability and oversight.
Another way to avoid ceiling debt is to increase borrowing capacity.
This can be achieved by improving credit ratings through sound fiscal policies, implementing structural reforms to boost the economy and attract investors, and negotiating favorable loan agreements with international financial institutions.
By implementing these measures, it is possible to effectively manage and avoid reaching ceiling debt.
What Are the Potential Solutions to Manage Ceiling Debt?
Potential solutions to manage ceiling debt include increasing revenue, reducing spending, and raising the debt ceiling.
- Increasing revenue: The government can generate more revenue by raising taxes or closing tax loopholes. This provides additional funds to manage the debt.
- Reducing spending: By implementing spending cuts in various sectors, the government can allocate funds towards debt repayment.
- Raising the debt ceiling: If the government reaches the federal debt ceiling, one solution is to raise it. This allows the government to continue borrowing money to meet its financial obligations.
However, it is important to note that these solutions can have implications and consequences.
Increasing taxes may burden individuals or businesses, while spending cuts can impact services and programs.
It may lead to concerns about the government’s ability to manage debt and affect investor confidence.
Policymakers must carefully evaluate the economic and social implications before implementing any measures to manage ceiling debt.
The Implications of Ceiling Debt
Ceiling debt is a critical issue that individuals should not overlook since it has significant implications for their finances.
It is crucial to be aware that ceiling debt can have adverse effects on borrowing capacity and credit ratings.
Moreover, it is important to note that ceiling debt can also have a detrimental impact on financial markets and investor confidence.
The uncertainty surrounding the debt ceiling can result in market volatility and higher borrowing costs for the government.
Failing to raise the debt ceiling can lead to defaulting on obligations, causing severe consequences for both the economy and individuals alike.
Therefore, individuals must stay well-informed about government actions and decisions regarding ceiling debt to make informed financial choices and plan accordingly to mitigate any negative effects that may arise.
How Does Ceiling Debt Affect Financial Markets?
Ceiling debt significantly impacts financial markets. Reaching the debt ceiling creates uncertainty and instability, making investors cautious about the government’s ability to pay its debts.
This can cause a decline in investor confidence, leading to lower stock prices and bond yields. Financial markets thrive on stability and predictability, so ceiling debt disrupts this.
It can increase interest rates, making borrowing more expensive for individuals and businesses. This can hinder economic growth.
Financial institutions heavily rely on government treasury bonds as safe investments, so uncertainty about debt payment can affect the entire financial system.
Ceiling debt can also result in credit rating downgrades, raising borrowing costs for the government and impacting overall creditworthiness.
Ultimately, it can decrease investment, reduce economic activity, and harm the economy’s health.
Pro tip: Investors must closely monitor debt ceiling discussions and decisions. Understanding the potential impacts on financial markets can help make informed investment decisions and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Fiscal Discipline
- Controlling Budget Deficits
- Investor Confidence
- Limiting Government Spending
- Encouraging Fiscal Reforms
- Political Gridlock
- Risk of Default
- Uncertainty in Markets
- Impact on Borrowing Costs
- Potential Impact on Economic Growth
- Inadequate Flexibility
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Ceiling Debt?
What are the long-term effects of ceiling debt? Increased interest payments are a long-term effect of ceiling debt. As the debt increases, the government must make higher interest payments, which could lead to increased taxes or reduced spending of the federal government in other areas.
Ceiling debt can also weaken the government’s credit rating, potentially making it more expensive for them to borrow money in the future.
Additionally, it can contribute to economic instability by hindering economic growth and investment, leading to slower economic development and lower employment rates.
High levels of ceiling debt can also limit the government’s ability to borrow in the future, making it harder for them to finance necessary projects or respond to economic downturns.
Furthermore, ceiling debt can strain social programs and public services, as the government prioritizes debt repayments over funding for education, healthcare, and other essential services, impacting the well-being of its citizens.
Some Facts About Understanding Ceiling Debt: What It Means for Your Finances:
✅ The U.S. debt ceiling is the maximum amount of money that the government can borrow to pay its bills.(Source: Our Team)
✅ Lawmakers are currently at an impasse in raising the debt ceiling, raising the prospect of a default on the U.S. debt as soon as June 1.(Source: Our Team)
✅ Defaulting on the U.S. debt could have serious economic repercussions, including recession, job loss, delayed federal benefits, higher borrowing costs, and a plunging stock market.(Source: Our Team)
✅ The U.S. government relies on debt to fund its obligations because its revenue is not enough to cover expenses.(Source: Our Team)
✅ Efforts to raise or abolish the debt ceiling have become a heated topic of debt ceiling debate among policymakers, with some lawmakers using negotiations on the debt limit to push for spending cuts.(Source: Our Team)
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding ceiling debt is paramount for comprehending its profound implications on both individual finances and the broader economy.
Ceiling debt represents the maximum borrowing limit set by the government, and reaching this limit can have dire consequences, including default on debts, credit rating downgrades, higher borrowing costs, and a loss of investor confidence.
Ceiling debt not only affects government operations but also has ripple effects on interest rates, financial markets, and overall economic growth.
It requires proactive and responsible financial management to avoid reaching the debt limit, necessitating measures such as fiscal policies promoting responsible spending, reduced budget deficits, and finding alternative revenue sources.
Furthermore, individuals must be aware of the impact of ceiling debt on borrowing power, credit ratings,and financial markets, as these factors can directly influence personal finances, investments, and economic stability.
To safeguard financial well-being, it is essential for individuals and policymakers to stay informed about government actions related to ceiling debt and work collectively to implement effective strategies for managing and avoiding its potential negative effects.
In a world where global financial stability is interconnected, addressing ceiling debt responsibly and transparently is crucial for securing a sound economic future for both individuals and nations.
By embracing fiscal discipline, prioritizing financial responsibility, and making informed decisions, we can navigate the challenges posed by ceiling debt and ensure a more resilient and prosperous financial landscape for generations to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
The debt ceiling refers to the maximum amount of money that the US government can borrow. It is a legal debt limit set by Congress on the total amount of debt the government can accumulate. If the US defaults on its debts, it can have catastrophic effects on the country and the global economy.
The debt limit has been raised 102 times since World War II. This is because the US government has been spending more than it collects in taxes, leading to the need for borrowing to cover budget deficits.
A default on US debts would have severe consequences. It could lead to the closure of government offices, loss of jobs, and a decrease in the desirability of American debt for international investors. The exact consequences are uncertain, but economists warn that it could result in a financial and debt ceiling crisis.
There have been several proposed solutions to raise the debt ceiling. These include a clean debt ceiling increase without conditions, spending cuts, using the 14th Amendment, introducing a bill, or minting a trillion-dollar coin. However, negotiations have been at a standstill, and a quick resolution is not expected.
Japan, China, and the United Kingdom are the top holders of US debt. The US government also owes money to itself, including the Federal Reserve and Social Security. Approximately 12% of the US budget is spent on interest payments.
A default could lead to a recession, job loss, delayed federal benefits, higher borrowing costs, and a plunging stock market. It could also result in a credit rating downgrade, affecting mortgages, credit cards, and other consumer debt. The precise scope of the consequences is unknown, but they are expected to have severe financial harm.