What is the difference between cash market and derivative market? Understanding financial markets can be quite a daunting task, especially when it comes to distinguishing the cash market from the derivative market. One critical fact is that these two markets differ profoundly in their operation and purpose.
This article is designed to break down these complexities for you, providing unique insights into their differences and potential benefits. Stay tuned as we embark on an exciting journey through the world of finance!
Key takeaways
●Cash markets deal with real goods like stocks. You buy these and own them for life.
●Derivative markets work with futures and options. Here, you bet on prices of goods rather than owning them.
●The cash market is less risky but offers less chance for quick gains, while the derivative market has more risk but can lead to big profits quickly.
●Investors pick which market to use based on what they want from their investment and how much risk they are ready for.
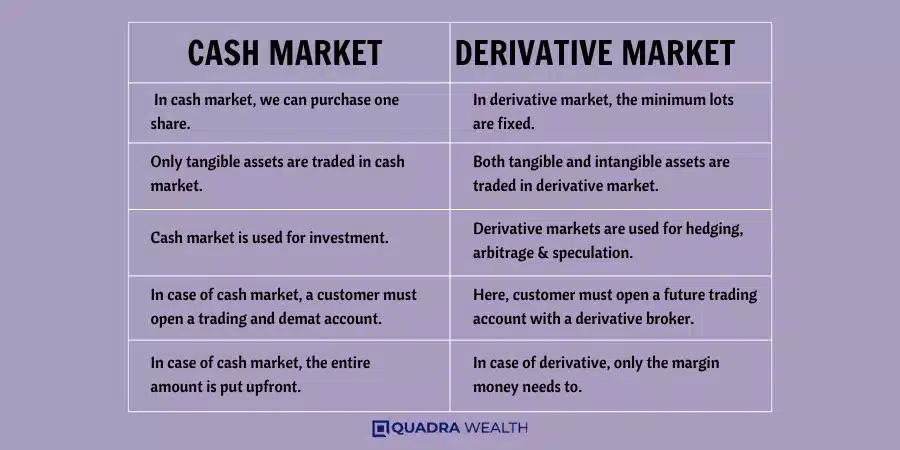
Difference Between Cash Market and Derivative Market
The cash market is a place where people buy and sell goods for immediate delivery. This means you pay cash right away and get your item at the same time. Items can be things like stocks, bonds, or other types of securities.
In this market, prices are set by how much buyers will pay and how little sellers will take. The Stock Exchange is an example of a cash market. Over-the-counter transactions also occur here.
This makes the cash market very liquid, meaning assets could easily be changed into cash if needed.
People who use this type of market want quick results or deals that don’t last long.
They can make use of short-term chances to earn money quickly because there’s no waiting period after buying something.
One key feature about this type of trading is that once you own an item, it’s yours forever unless you decide to sell it again later on! You also get any dividends that come with owning those items which add more value over time.

Exploring the Derivative Market
The derivative market is a busy place. It’s where people buy and sell futures and options. These are types of contracts, not actual goods or stocks.
The price of these contracts depends on something else, like a stock or commodity. This other thing is called an “underlying asset”.
There are two kinds of this market: exchange-traded and over-the-counter (OTC). Exchange traded derivatives have set rules and are more formal.
OTC markets can be less rigid but also riskier.
In this market, you’re not aiming to own the underlying asset forever. Your goal is to make money from changes in its price before the contract ends.
People use derivative markets for three main things: hedging risk, speculating on future prices, and trying to make a quick profit (arbitrage).
The potential profits here can be big because you don’t need much money to start off with – that’s leverage for you! But remember there can be high risks too if things go opposite as planned.
So now you know what goes on in the world of derivative trading!

Key Differences Between Cash Market and Derivative Market
Discover how cash and derivative markets vary in aspects like asset nature, investment purpose, delivery of assets, costs involved, and associated risks; each contributing to a unique investing experience.
Dive deeper into the heart of financial trading through the following sections!
Nature of assets traded
In the cash market, we usually trade actual assets. These could be things we can touch and see, like cars or houses.
This is different in the derivative market. There, people deal in both seen (tangible) and unseen (intangible) items.
It’s not just about physical stuff! The derived value of these goods is what matters here.
Timelessness of assets vs. expiry dates
In the cash market, assets never expire. You buy things like stocks and they are yours for good.
This is not the case in the derivative market. Here, deals close after a fixed time frame.
So, while you have ownership forever in the cash market, it’s short-term in the derivative market.
Presence of IPOs in cash market
IPOs, or Initial Public Offerings, are found in the cash market. This is where new firms first sell their shares to the public. The money from these sales goes straight into the firm’s funds.
People buy IPOs hoping that the company will grow and make more money over time. In turn, this will raise the value of their shares.
These shares then can be sold on an ongoing basis in secondary trading on a cash market platform like a stock exchange.
Backing of equities with business in cash market
In the cash market, firms back their equities with business. This means they use company assets or operations to support their stock.
It offers more fluidity to investors and a chance to gain from short-term movements. Cash markets list real prices for shares backed by businesses.
These stocks are ready for instant delivery upon buying them. This allows buyers of these equities to be true owners right away.
With this, they can enjoy dividends that come with owning such assets.
Derivation of value: company value vs. underlying asset
In a cash market, the value of a company decides its price. A strong business means more worth for its stock. In a derivative market, it works differently.
Here deals are made using assets like stocks but their worth comes from something else. This “something else” is called the underlying asset.
The price of this asset gives the derivative its value. So, in simple words, cash markets use how well the company does to get prices and derivative markets look at other items’ values for setting prices.
Availability of leverage
In the derivative market, you can use leverage. Leverage lets you handle more assets without much cash. For example, a small amount of money can control a large futures contract.
This is not possible in the cash market where full payment is needed for each deal. But be careful! Using leverage can make your profits bigger but it can also increase your losses.
In other words, if things don’t go as planned, you could lose more than your first investment. So, always take care when using leverage in derivative markets to manage risk and aim for higher returns.
Purpose of investment: value accretion vs. speculation, hedging or arbitrage
You need some papers to start a SIP investment. First, get your PAN card and bank details ready. You also need an address proof like a utility bill or Aadhar Card. If you are new, fill out the KYC form online.
Always check all your data on these papers before moving to the next step.
Purpose of investment: value accretion vs. speculation, hedging or arbitrage
In cash markets, people buy assets to grow their value over time. They hope the price will go up. This idea is called “value accretion”.
On the other hand, in derivative markets, people try to make quick money. They use tools like “hedging” and “arbitrage”. Hedging lets them protect against price changes.
Arbitrage lets them take advantage of different prices in different places at once. These kinds of trades are often seen as guesses or bets (“speculation”).
So it’s important for each investor to think hard about what they want from their investment before they decide where to put their money!
Delivery vs. non-delivery of assets
Cash markets deal with the delivery of assets. When you buy a share, for example, you get it right away. You become its rightful owner and enjoy all benefits that come with it.
Derivative markets work differently. Here, you buy or sell an asset’s promise for a future date. But this doesn’t mean taking actual ownership or getting delivery of the asset itself immediately.
The focus here is on dealing with price moves in the future, not owning any assets now.

Comparative costs
In the cash market, you pay less costs. Brokerage rates are lower. But in the derivative market, you pay more fees like STT (Securities Transaction Tax).
You also need to keep funds ready for margin trading. This is a big cost that can add up over time. So, the cash market may be cheaper at times.
But it does not offer as much leverage as the derivative market does.
Risk scale: equity vs. derivatives
Equity and derivatives vary in their risk scale. Buying shares of a business is less risky. It’s because you become part owner of the company. You also get the reward when the company makes profit.
Yet, market factors can change stock prices too.
Derivatives are different – they carry more risk than equities. Risk here means loss of money invested if things don’t go as planned or hoped for.
Some people may make more money from derivatives than from equities, though it’s not always true for all investors out there! So, investing in derivative markets will have more ups and downs compared to equity markets.
Benefits of Investing in Cash Market
Investing in the cash market can offer many gains to traders. The following are some key benefits:
- Assets in a cash market are delivered right away.
- Traders have the chance to make smart choices with real – time prices.
- The flexibility is high and allows for gains on short – term changes.
- Traders who own the asset get to receive dividends.
- No need to deal with data or paperwork as everything is clear and straightforward.
- Cash markets allow buying of single units, not only lot sizes.
- Allows building of a strong and quality portfolio over time due to ownership of assets.
- Provides lower amount of risk compared to derivative markets due to the nature of tangible assets being traded.
Advantages of the Derivative Market
The Derivative Market has many benefits. These include:
- It lets people manage risk. They use it to bet on changes in values.
- The chance of getting a high return is higher than the risk taken.
- Investors can trade in two types of markets: Exchange Traded Derivatives and Over-The-Counter derivatives.
- People do not own the items they bet on, they only deal with contracts.
- This type of market uses a future trading account.
- There is no need for full money up front, making it easier to start trading.
- It helps make other markets move as well. This is done by guessing the right price for items.
Making the Choice: Cash Market or Derivative Market?
Every person has a different goal for their money. Some like safe bets, others enjoy risk. The cash market can offer less worry.
In this market, you buy goods right away and become the owner of these goods. On the other hand, the derivative market comes with high risks but also high gains.
Here, people bet on future prices of assets instead of buying them on spot. You don’t own the asset but rather hold a contract that could profit from price changes in the future.
There’s no wrong choice; it rests upon your risk tolerance and financial goals. If safety is top priority, cash markets may be best for you because they offer actual asset ownership and dividends often come into play too.
If you love challenges and have room for risk, then dive into derivatives! Potential profits can soar here when dealt wisely but remember there are chances you might lose too if bets go wrong.

Conclusion
So, the cash and derivative markets are both important. They have different uses for people who want to invest money.
Choose the market that fits your needs best after you learn about them.
FAQs
The cash market is where you buy or sell commodities for actual prices. In contrast, the derivative markets let you trade through futures or other derivatives instruments.
In a cash market, lifetime ownership of commodities like Infosys shares happens right after full payment. In derivatives, trading depends on an underlying asset’s value till expiry of a maturity period.
Both markets help with risk management and efficient capital allocation but in different ways. Cash markets provide liquidity advantage while Derivatives assist with hedging of risk.
Yes! For cash trades, you need a Demat account to hold intangible assets like equity indices while no specific type of account is needed for derivatives because they don’t involve owning physical goods.
Spot futures arbitrage involves buying single units from the spot(Cash) market and selling them at higher prices in derivatives using real-time price discovery techniques.
Yes! Both can affect business value by enabling diversification into timeless assets or creating diverse quality portfolios depending on intrinsic values.









