Introduction
Well, what is your understanding of principal-protected notes (PPNs)? PPNs are notes in which investors’ capital wallets are protected to a greater extent.
While the derivative component of the PPN protects capital, the assets determine the returns of investment for PPNs.
On this parlance, let us deep dive the blog title: ‘What Are Principal Protected Notes?’ Helping you get started further:
Structure of PPNs
How are PPNs structured? Let us have a rundown of pointers that are connected with the same:
Principal Protection
Potential Upside
PPNs have underlying assets that comprise capital-protected stocks, fixed-income securities, and a basket of investment bonds. These assets underlie the PPNs and provide an upside potential for the notes to earn better rates of return. The investors of PPNs, therefore get better rates of return as compared to traditional bonds or fixed-income securities.
Maturity period
PPNs have longer maturity periods embedded in them by product-issuing firms. This is primarily because the investor’s capital cannot be protected against short-term investments. You require a long-term holding to protect your investments and provide you with a more stabilized financial portfolio. Hence, PPNs are long-term investment options you can have hands-on.
Value of the notes at the time of redemption
The performance of the underlying assets at the time of redemption against capped returns, as decided by product issuers, determines the value of the notes investors get while these PPNs are up for redemption. The value of PPNs would surpass the initial investment values done at the time of signing up.
How Do PPNs Work?
Here is how PPNs work for the investors on the whole. Here is a rundown of pointers that are connected with the same:
Investment Allocation
The assets are carefully evaluated before the product issuers embed them or underlie them to PPNs. The assets would then be scrutinized against how capital safe they are.
The PPNs would typically comprise capital-safe investments like a basket of corporate and government-aided bonds, mortgages, capital-safe equities, and fixed-income securities.
This is because the notes have to provide 100% capital protection when investors opt for redemption. But sometimes, upon the request of investors, these notes can also comprise of market stocks, commodities, or currencies to name a few.
Return Calculation
The rate of returns for PPNs is usually determined at the inception stage when the notes are being designed. The product-issuing firms and investors sit hand-in-hand to discuss the rates of return these PPNs must yield on their investment portfolios. The RoI of the notes are decided at the beginning stages of offer document curation itself.
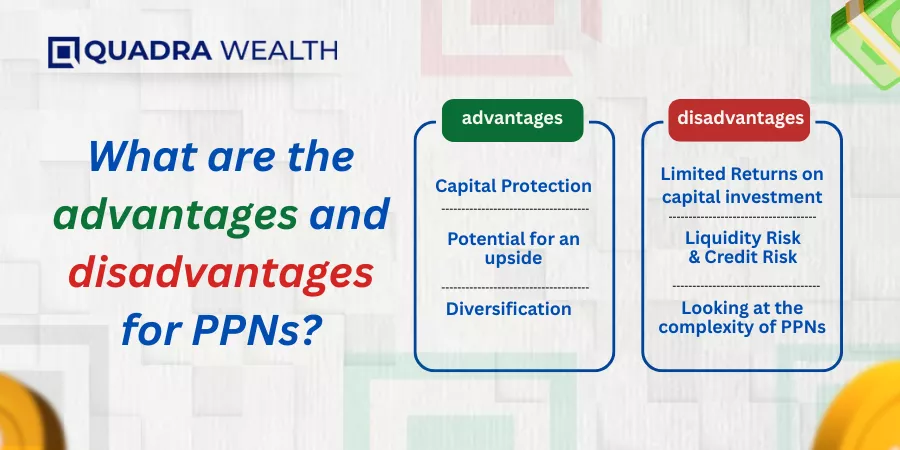
What are the primary advantages for PPNs?
These are the primary benefits of PPNs. Let us have a rundown into the same:
Capital Protection
The Principal Protection or the capital protective nature of PPNs is what appeals to investors the most. Traditional retail investors, pensioners, and retirees save several years of their job-related income to arrive at a corpus amount that they deposit in lieu of PPNs. Under no circumstances are they ready to lose even a tiny portion of their cap wallet.
Potential for an upside
The capped returns and the principal amount are what the investors would get at the time of redemption. However, if the underlying assets of PPNs perform well, you can access the higher market potential the notes earn. A few firms can even offer capital reimbursements like dividend earnings if the underlying assets perform really well inside the marketplace.
Diversification
PPNs allow investors to have access to different financial products without needing to make direct investments into each one of them. Therefore, the PPNs allow investment portfolios to grow at an exponential scale, and you create diversified portfolios that help you clear your financial obligations in a streamlined manner indeed.
What are the disadvantages of PPNs?
These are the prime disadvantages associated with PPNs. Let us have a rundown into the same:
Limited Returns on capital investment
PPNs have limited potential to earn returns on highly performing market assets. This is because capped returns or ceiling limits are incubated on PPNs by product issuers. Therefore, you have the returns limited to the capped values, even if the underliers perform exceedingly well in the market.
Liquidity Risk
The PPNs have to be held until the period of maturity and cannot be sold easily before then. Even if you try selling PPNs in secondary markets, you may incur significant losses over their capital value.
Looking at the complexity of PPNs
PPNs are structured notes that comprise a mix of fixed and derivative components. These notes are, therefore, complex for a newbie or an amateur investor to learn or understand.
Credit risk
PPNs are subject to the credit risk of the issuing company. If the product issuer falls defunct due to insolvency or liquidity issues, then investors face the risk of losing their partial or even complete value of their investment capital.
What are the common features of PPNs?
These are the common features that are associated with the issuance of PPNs. Let us have a rundown into the same:
Payment of coupons
Investors of PPNs are offered with periodic coupons as and when the product issuers state the issuance of coupons on offering documents. The coupons may be at par or lesser than bonds or interest-bearing securities.
Participate rate
PPNs are subject to limited potential to earn returns on investments, even if the underlying assets perform well in the market. The returns are usually limited or restricted to RoI levels as was designed on the notes while they were being incubated.
Say, for instance, if the PPNs are offered with a 60% return on the participating assets, then the investors would get 60% returns on the performance of the underlying assets.
Capped returns
Whatever the designated returns on your PPNs, the returns would be limited to this potential only, even if the underlying assets of the notes perform exceedingly well.
Who should consider PPNs?

These are the types of investors that usually prefer investing their money into PPNs. Let us look at what category of people these investors belong to. Helping you through, with a rundown into the same:
Conservative Investors
PPNs highly appeal to conservative investors who may want protection of their capital investment and oversee potential returns on the capital investments that they have made.
Risk-Averse Investors with a Market View
PPNs highly appeal to investors who want an overview or a long-sighted view of how equity markets work. This is because you find that PPNs are linked with capital safe equities or indexes that show better stability in the overall marketplace.
Say, for instance, your S&P 500. This is an index that clusters 500 of the best-performing entities across the globe. Therefore, the index remains stable unless you find a market crash in the name of recession or arrive at unprecedented economic downturns.
Long term investors
PPNs are more suitable for conservative retail investors like senior citizens, pensioners, or retirees who would want to lock up their funds safely and can wait until the notes mature. Therefore, PPNs are meant for long-term investors who look for credibility and the safety of their capital or principal investment.
The Bottom Line
The overall know-how on how PPNs work in an economic strata has been discussed with you on a comprehensive scale.
These notes typically work like traditional bonds or fixed-income securities that guarantee principal investment plus give you a hindsight overview on how structured products operate across investment markets.
Frequently Asked Questions or FAQs

Should the amount invested for PPNs be held to maturity?
Answer: Yes, the PPNs are notes that must be held until maturity if you want to receive your minimum investment and interest earnings as the cummumulated payouts.
Do mutual fund companies handle the issuance of PPNs?
No, Mutual Funds operate differently from how structured notes operate in the market. Wealth Management firms, investment-grade banks and private practitioners gain primary clients for notes and charge a fee in lieu of the same.





