In This Article
The Ultimate Guide to Structured Product Pricing!

The Pricing structured product is a complex and specialized field in the realm of finance. It requires a deep understanding of various factors and methodologies to accurately determine the value of these products.
In this comprehensive guide, we will provide an overview of the pricing structured product, including their basics, factors influencing their pricing, common pricing models, pricing in different financial markets, advanced pricing techniques, and risk management and evaluation of pricing models.
An Introduction to Structured Product Pricing
Structured products are hybrid financial instruments that combine traditional investments, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities, with derivatives.
They offer customized investment strategies that cater to specific investor needs. To effectively price structured products, an understanding of their underlying components, payout structures, and market dynamics is essential.
Understanding the Basics of Structured Products
To gain a solid understanding of structured products, it is essential to examine their key components: underlying assets, payoff structure, and features.
Component | Description |
|---|---|
Underlying Assets | Structured products derive their value from various assets, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities. |
Payoff Structure | The payoff structure determines how structured products generate returns. It can be linked to the performance of the underlying assets, a fixed rate, or a combination of both. |
Features | Structured products often offer additional features, such as principal protection or participation in market gains. These features can vary depending on the specific product. |
Having a clear understanding of these basics is crucial before delving into the intricacies of the pricing structured product. By comprehending the underlying assets, payout structure, and features, investors can make informed decisions.
Pro-tip: When evaluating structured products, consider your risk tolerance and investment objectives. Additionally, carefully analyze the potential returns and associated costs to make a well-informed investment decision.
What Are Structured Products?
Structured products, such as notes, certificates, or funds, are complex financial instruments that are created by combining different financial assets to meet specific investment goals or to provide customized investment solutions.
They are designed to provide investors with exposure to multiple underlying assets and offer potential returns based on the performance of those assets. Structured products can be linked to various asset classes such as equities, fixed-income securities, commodities, or currencies.
Their predefined terms and conditions, including the maturity date, coupon rate, or participation rate, make structured products unique. Depending on the investor’s risk appetite and investment objectives, these products can offer features like capital protection, downside risk mitigation, or leverage.
However, it’s important to note that structured products require a thorough understanding of the underlying assets and the structure of the product itself.
While they may not be suitable for all investors and require a higher level of investment knowledge and risk tolerance, investors can make informed decisions by understanding what structured products are and their key features.
Before investing in structured products, consulting with a qualified financial advisor or conducting thorough research is essential.

Types of Structured Products
Structured products come in various types, which can be classified into four broad categories: equity-linked structured products, fixed-income structured products, commodity-linked structured products, and currency-linked structured products.
Category | Description |
Equity-Linked Structured Products | These structured products are directly linked to the performance of underlying stocks or equity indices. They provide investors with exposure to equity markets while incorporating structured payoffs based on predefined conditions or scenarios. |
Fixed-Income Structured Products
| These structured products revolve around fixed-income securities, such as bonds or interest-rate derivatives. They enable investors to customize their exposure to fixed-income markets while potentially enhancing yield or managing risk.
|
Commodity-Linked Structured Products | Commodity-linked structured products are tied to the price movement of commodities, including oil, gold, or agricultural products. They allow investors to gain exposure to commodity markets while providing structured payoffs linked to commodity price fluctuations. |
Currency-Linked Structured Products | Currency-linked structured products involve currency pairs and offer investors exposure to foreign exchange markets. They can be structured in a way that provides investors with hedging capabilities or opportunities to profit from currency movements. |
Understanding the various types of structured products is crucial for investors in order to choose the ones that align with their investment objectives, risk appetite, and secondary market outlook.
Structured products have gained popularity in recent years due to their potential for customized investment solutions. Investors have increasingly sought to diversify their portfolios and capture market opportunities beyond traditional investments. Consequently, financial institutions have developed a wide range of structured products to meet the demand for tailored investment strategies.
Why Are Structured Products Popular?
Structured products are popular for several reasons in the financial markets. Why are structured products popular? Firstly, they offer investors the opportunity to customize their investment strategies according to their risk appetite and financial goals.
This flexibility allows investors to tailor their portfolios to meet specific needs. Secondly, structured products provide access to a wide range of underlying assets, including equities, fixed-income securities, commodities, and currencies.
This diversification potential allows investors to spread their risk and potentially enhance their returns. Why are structured products popular? Another reason for their popularity is their potential for higher returns compared to traditional investments.
By incorporating derivatives and complex payout structures, structured products offer the possibility of higher yields and enhanced performance. Furthermore, structured products often provide investors with exposure to unique investment themes and strategies that are not readily available through other investment vehicles.
This novelty and exclusivity attract investors who are looking for innovative investment opportunities. Lastly, structured products can also offer downside protection through features such as capital guarantees or buffer zones.
These risk mitigation features make structured products attractive to investors who want to limit their losses in volatile market conditions. Why are structured products popular?
The combination of customization, diversification, potential for higher returns, unique investment opportunities, and downside protection make structured products a popular choice among investors.

Factors Influencing the Pricing of Structured Products
Pricing a structured product is no easy task, as it depends on a multitude of factors that can make or break the value. In this section, we will explore the various elements that play a crucial role in determining the price of structured products.
From market factors and underlying asset characteristics to the intricacies of structured product design and the ever-changing economic climate, we’ll delve into the key influencers that shape the pricing landscape.
Get ready to uncover the fascinating dynamics that drive the pricing of structured products.

Market Factors
To understand the pricing of structured products, it is crucial to consider various market factors. These market factors, including interest rates, volatility, market liquidity, market sentiment, and underlying asset prices, can have a significant impact on the value and performance of structured products.
Market Factors | Description |
Interest Rates | Changes in interest rates can affect the pricing of structured products, especially those with fixed-income components. Higher interest rates can result in lower prices for fixed-income structured products. |
Volatility | Market volatility, which is a measure of money fluctuations, can impact the pricing of structured products. Higher volatility can increase the value of options embedded within the product. |
Market Liquidity | The ease with which structured products can be bought or sold in the secondary market can impact their pricing. Higher liquidity generally leads to more efficient pricing. |
Market Sentiment | Investor sentiment and market expectations can influence the demand and pricing of structured products. Positive sentiment can drive up prices, while negative sentiment can lead to lower money. |
Underlying Asset Prices | The prices of underlying assets, such as stocks or commodities, can affect the value of structured products linked to them. Changes in asset prices can result in changes in the product’s value. |
An interesting fact about market factors is that the pricing of structured products is not solely determined by the issuer or the product design. External market conditions play a crucial role in their valuation and performance.
Underlying Asset Characteristics
Asset Type | Characteristics |
Equities | Ownership shares in a company, representing a claim on its assets and earnings. Characteristics include price volatility, dividend yield, and market capitalization. |
Bonds | Debt securities issued by governments or corporations. Characteristics include coupon rate, maturity date, credit rating, and yield to maturity. |
Commodities | Physical goods are used for commerce or as inputs in the production process. Characteristics include supply and demand dynamics, storage costs, and seasonality. |
Currencies | Forms of money are used as a medium of exchange. Characteristics include exchange rates, interest differentials, inflation rates, and political stability. |
Understanding the underlying asset characteristics is crucial in pricing structured products. Each asset type has its own unique features that can impact the pricing and risk profile of a structured product.
Equities, with their money volatility and dividend yield enhancement products, can provide the potential for initial capital gains and income. Bonds, on the other hand, offer more stable returns through coupon payments and the return of principal at maturity.
Commodities, such as gold or oil, are influenced by factors like supply and demand, creating opportunities for profit in commodity-linked structured products.
Currencies are affected by economic and political factors, making currency-linked structured products sensitive to changes in exchange rates and interest differentials.
By considering these underlying asset characteristics, investors can tailor their structured product investments to align with their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Whether seeking growth, income, or diversification, understanding the unique properties of each asset type allows for informed decision-making.
It is essential to analyze the historical performance and future prospects of the underlying assets to accurately price structured products and assess their potential returns.
Structured Product Design
When considering structured product design, it is essential to prioritize Structured Product Design to meet individual investor needs and preferences. Effective risk management must be integrated to ensure appropriate risk-return profiles and capital protection mechanisms.
The level of complexity should be considered, and it is crucial to select products that align with one’s risk tolerance and investment objectives. Lastly, transparency plays a vital role in understanding the product’s features, risks, and potential returns.
By evaluating these factors, investors can make informed decisions and choose structured products that align with their goals and risk appetite.
Economic Factors
1. Market conditions: Economic factors such as interest rates, inflation levels, and overall market volatility impact the pricing of structured products. For example, when interest rates are low, structured products with fixed-income components may offer lower returns.
2. Investor demand: Economic factors, including investor sentiment and risk appetite, influence the demand for structured products. In times of economic uncertainty, investors may seek structured products that provide downside protection or have lower risk characteristics.
3. Underlying asset performance: Economic factors affecting the performance of underlying assets, such as stock market prices, commodity prices, or currency exchange rates, directly impact the pricing of structured products linked to those assets. For example, a structured product linked to the performance of a specific stock will be influenced by the stock’s price movements.
4. Regulatory environment: Economic factors can be influenced by regulatory changes, such as new laws or regulations impacting financial markets. These regulatory changes can affect the pricing and design of structured products, as issuers may need to comply with new requirements.
Pro-tip: When considering economic factors in the pricing of structured products, it’s important to stay informed about market conditions, investor sentiment, and regulatory developments. This knowledge will help you make informed decisions and effectively evaluate the potential risks and returns associated with structured products.
Common Pricing Models for Structured Products
Discover the power behind common pricing models for structured products as we dive into the world of financial valuation. From the Black-Scholes Model to Monte Carlo Simulation, and the Binomial Model to Lattice-Based Models, we’ll explore a range of techniques that shape the pricing landscape.
Stay tuned to unravel the strategies and formulas used by financial experts to determine the value of these intricate investment vehicles. Prepare to be amazed by the precision and complexity that lies within these pricing models.

Black-Scholes Model
The Black-Scholes Model, also known as the Black-Scholes pricing model, is a widely used tool in the financial industry to determine the theoretical value of options and derivative securities.
| Black-Scholes Model |
Definition: | The Black-Scholes Model is a pricing model used to calculate the theoretical value of options and derivative securities. |
Application: | The Black-Scholes Model is widely used in financial markets to price options on stocks, currencies, commodities, and other assets. |
Assumptions: | The Black-Scholes Model assumes that the financial market is efficient, there are no transaction costs, and there are no restrictions on short selling. It also assumes that the underlying asset follows a log-normal distribution and that there is no dividend payment during the option’s life. |
Components: | The Black-Scholes Model takes into account factors such as the current price of the underlying asset, the option’s strike price, the time to expiration, the risk-free interest rate, and the volatility of the underlying asset. |
Output: | The Black-Scholes Model provides an estimate of the fair value of the option, which can be compared to the competitive market money to determine whether the option is overvalued or undervalued. It also calculates the option’s sensitivity to changes in the underlying parameters, known as the Greeks (Delta, Gamma, Vega, Theta, and Rho). |
Usage: | Investors and financial institutions use the Black-Scholes Model to make informed decisions about buying, selling, or trading options. It is also used by academics and researchers to study the behavior of financial markets. |
Monte Carlo Simulation
The Monte Carlo Simulation, a powerful tool used in the pricing of structured products, involves the following steps:
- Define the parameters: Determine the inputs required for the simulation, such as the underlying asset price, volatility, and time horizon.
- Generate random scenarios: Using a random number generator, create a large number of possible scenarios for the underlying asset’s future price movement.
- Calculate payoffs: For each scenario, calculate the payoff of the structured product based on its specific payoff structure.
- Aggregate payoffs: Sum up the payoffs from all the scenarios to obtain the expected value of the structured product.
- Apply to discount: Discount the expected payoff to the present value to account for the time value of money.
- Repeat the process: The Monte Carlo Simulation is typically repeated multiple times to improve accuracy and reduce bias.
The Monte Carlo Simulation was named after the Monte Carlo Casino in Monaco, famous for its games of chance. This simulation method was developed in the 1940s by scientists working on the Manhattan Project to model the behavior of neutrons within a nuclear reactor.
Since then, the Monte Carlo Simulation has become widely adopted in various fields, including finance, to analyze complex systems and calculate probabilities.
The Monte Carlo Simulation is particularly useful in the pricing structured product as it allows for a comprehensive assessment of potential outcomes and helps investors make informed decisions.

Binomial Model
The Binomial Model is a widely used pricing model in finance that is utilized to determine the value of options and other derivatives. It is based on the assumption that the price of the underlying asset will either increase or decrease by a certain percentage over a specific period of time.
Key Features of the Binomial Model
1. The model assumes that the price of the underlying asset can only move up or down in discrete time intervals.
2. It incorporates the concept of risk-neutral probabilities, which allow for the calculation of the expected value of the option.
3. The model uses a binomial tree structure, where each node represents a possible price of the underlying asset at a specific point in time.
4. The valuation of the option is done by working backward through the tree, calculating the option value at each node based on the probabilities of the underlying asset’s price movement.
5. The Binomial Model can handle options with early exercise features, such as American options, making it a versatile pricing tool.
6. The model requires assumptions about the volatility of the underlying asset and the risk-free interest rate to accurately calculate option prices.
7. It is computationally intensive, as the number of nodes in the tree increases with the complexity of the option.
8. The Binomial Model can be used to price a wide range of derivatives, including options on stocks, currencies, commodities, and more.
The Binomial Model provides a valuable tool for investors and financial professionals to determine the fair value of options and make informed investment decisions. Its flexibility and ability to handle various option types make it a key component in the field of structured product pricing.
Lattice-Based Models
In the realm of the pricing structured product, lattice-based models are extensively utilized. This particular approach involves the construction of a lattice or grid structure, which effectively represents the possible price movements of the underlying asset over a specified period of time.
Within this lattice, each node corresponds to a specific price level at a given point in time. The creation of the lattice takes into account various parameters such as volatility, interest rates, dividends, and other pertinent market factors, allowing for the computation of potential price movements.
The intrinsic benefit of lattice-based models lies in their ability to simulate future price movements of the underlying asset. As a result, they facilitate comprehensive pricing calculations and risk analysis across a diverse range of scenarios.
When compared to simpler models like the Black-Scholes model, lattice-based models offer a more precise representation of market dynamics. This increased accuracy makes these models well-suited for pricing options with intricate features such as early exercise, barriers, and path dependency.
When employing lattice-based models for the pricing of structured products, it is crucial to consider the granularity of the lattice. While a larger number of nodes can enhance accuracy, it may also result in increased computation time.
Moreover, proper calibration of model parameters is paramount in order to achieve pricing results that accurately reflect the market dynamics.
Pricing Structured Products in Different Financial Markets
When it comes to pricing structured products in different financial markets, there are various approaches to consider. We’ll explore the intriguing world of equity-linked structured products, fixed-income structured products, commodity-linked structured products, and currency-linked structured products.
Buckle up as we dive into the fascinating realm where financial markets meet innovative pricing strategies. Get ready to uncover the secrets behind these distinct types of structured products and how they shape the ever-evolving financial landscape.
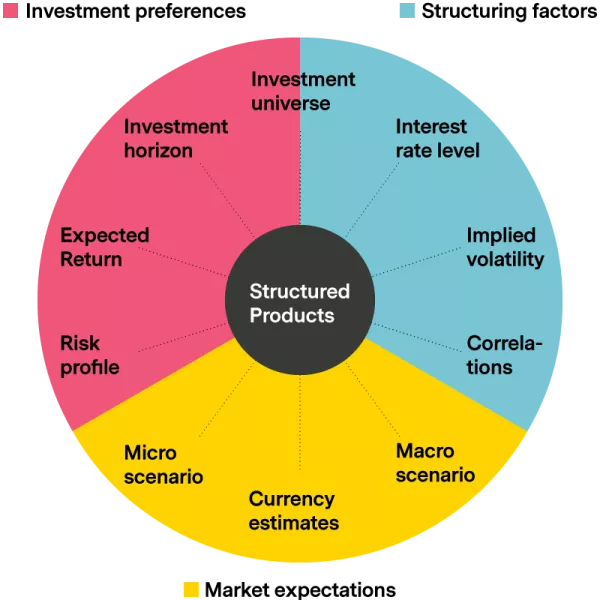
Equity-Linked Structured Products
When it comes to equity-linked structured products, it is important to understand the features and benefits they offer. These products are investment vehicles that combine a traditional fixed-income instrument with an equity derivative component.
Features | Benefits |
1. Linked to the performance of an underlying equity or a basket of equities. | 1. Allows investors to participate in the potential upside of the equity market. |
2. Typically have a specified maturity date. | 2. Provides investors with a defined investment period. |
3. May offer a guaranteed minimum return or downside protection. | 3. Offers investors a level of security in case of market downturns. |
4. May include additional features such as coupons or dividends. | 4. Provides investors with potential income streams in addition to the equity-linked return. |
Equity-linked structured products are popular among investors seeking a balance between potential returns and risk. They allow investors to diversify their portfolios and benefit from the performance of equity markets.
However, it’s important to carefully assess the terms and conditions of these products, including the underlying equities, the maturity date, and any potential downside risks.
Did you know? Equity-linked structured products accounted for approximately 30% of the structured products market in 2020.
Fixed-Income Structured Products
Fixed-income structured Products can be an attractive investment option for those seeking a steady income stream with potentially higher returns than traditional fixed-income securities. In this type of structured product, the underlying asset is typically a fixed-income security, such as a bond or a basket of bonds.
The issuer of the Fixed-Income Structured Product combines the fixed-income asset with derivative instruments to create a custom investment product.
When considering Fixed-Income Structured Products, it is important to analyze the specific features and characteristics to make an informed investment decision.
Here is a table highlighting key considerations for Fixed-Income Structured Products:
Features | Description |
Underlying Asset | The fixed-income security or securities that form the foundation of the Fixed-Income Structured Product. |
Derivative Instruments | The derivatives are used to enhance the returns or modify the risk profile of the Fixed-Income Structured Product. |
Payoff Structure | The specific conditions that determine the payout or return of the Fixed-Income Structured Product. |
Risk Profile | The level of risk associated with the Fixed-Income Structured Product, including credit risk and interest rate risk. |
Issuer Credit Rating | The creditworthiness of the issuer indicates the likelihood of fulfilling the payout obligations of the Fixed-Income Structured Product. |
Investment Horizon | The recommended holding period for the Fixed-Income Structured Product to achieve the intended returns.
|
By considering these factors, investors can evaluate the suitability of Fixed-Income Structured Products based on their investment goals and risk tolerance.
It is crucial to carefully review the terms and conditions, consult with financial professionals, and conduct thorough due diligence before investing in Fixed-Income Structured Products.
Commodity-Linked Structured Products
Commodity-Linked Structured Products can be a valuable addition to an investment portfolio, offering exposure to the commodities market while providing structured returns. These products are designed to track the performance of various commodities, such as crude oil, gold, or agricultural products.
To better understand Commodity-Linked Structured Products, consider the following table:
Product | Description | Performance |
Crude Oil-Linked Note | A structured product tied to the price of crude oil. | Returns are based on the changes in crude oil prices. |
Gold-Linked Certificate | A certificate that tracks the price movements of gold. | Investors can benefit from the appreciation of gold prices. |
Agricultural Futures Fund | A fund that invests in agricultural futures contracts. | Performance is tied to the prices of agricultural commodities. |
Commodity-Linked Structured Products offer investors an opportunity to diversify their portfolios and potentially profit from commodity price movements.
However, it’s important to note that these products come with risks, including market volatility and commodity price fluctuations. Investors should carefully evaluate their risk tolerance and conduct thorough research before investing in commodity-linked structured products.
By understanding the nuances of Commodity-Linked Structured Products and their potential benefits and risks, investors can make informed decisions when incorporating them into their investment strategy.
Currency-Linked Structured Products
When it comes to currency-linked structured products, there are certain factors that need to be considered in order to make informed decisions. Here is a table that highlights these factors:
Factor | Description |
Underlying Currency | The specific currency to which the structured product is linked. It could be a major currency like the US Dollar or a foreign currency. |
Exchange Rate | The rate at which the linked currency is exchanged for the base currency. This determines the return on the structured product. |
Interest Rates | The interest rates in the base currency and the linked currency can impact the returns of the structured product. |
Market Volatility | The level of fluctuations in the foreign exchange market can affect the performance and pricing of currency-linked structured products. |
Tenure | The duration for which the structured product will be held. Longer tenures may provide more potential returns but also involve higher risks. |
Considering these factors, investors can assess the potential risks and returns associated with currency-linked structured products. It is important to carefully analyze the market conditions and the outlook for the linked currency before making any investment decisions.
Pro-tip: Before investing in currency-linked structured products, it is advisable to consult with a financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance based on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
Advanced Pricing Techniques for Structured Products
Unlocking the hidden potential of structured products requires a deep dive into advanced pricing techniques. In this section, we’ll explore the captivating world of volatility smile and skew, correlation and copula models, credit risk and default models, and the intriguing process of pricing exotic structured products.
Get ready to embark on a journey that will shed light on the intricate dynamics and fascinating methodologies behind the pricing of these complex financial instruments. Prepare to be amazed!
Volatility Smile and Skew
When it comes to the pricing structured product, understanding the concept of volatility smile and skew is crucial.
Volatility Smile | The volatility smile refers to the graphical representation of implied volatility for options with the same expiration date but different strike prices. It takes the shape of a smile, with higher volatility for at-the-money options and lower volatility for out-of-the-money and in-the-money options. |
Volatility Skew | The volatility skew is a similar concept to the volatility smile but focuses on options with the same strike price but different expiration dates. It represents the difference in implied volatility between options with shorter expiration dates and options with longer expiration dates. |
The volatility smile and skew are observed in financial markets and indicate the market’s expectation of future volatility, as well as the pricing of options. These phenomena are important for the pricing structured product as they affect the valuation of the underlying options used in the product’s structure.
It’s important for investors and traders to closely monitor the volatility smile and skew as they can provide insights into market sentiment and potential opportunities for trading strategies. Understanding the shape and dynamics of the volatility smile and skew can help in assessing the risks and potential returns associated with structured products.
Fact: Market participants often refer to the volatility smile and skew as the “fear gauge” as they can depict the market’s perception of potential market downturns or events that could impact volatility.
Correlation and Copula Models
Correlation and copula models, being important tools, play a crucial role in the pricing and risk management of structured products.
Correlation Models: | Correlation models are widely used to assess the relationship between different variables, including asset prices or market indices. These models help quantify the degree of dependence or co-movement between the variables, facilitating more informed decisions for portfolio diversification. Moreover, correlation models enable the pricing of structured products linked to multiple assets, such as basket options or index-linked securities. |
Copula Models: | Both correlation and copula models are vital in the pricing and risk management of structured products. They provide better insights into the relationship between different variables, empowering investors to make sound investment decisions. By integrating these models into the pricing process, financial institutions can deliver accurate valuations for structured products, ensuring adequate compensation for the risks involved. |
Both correlation and copula models are vital in the pricing and risk management of structured products. They provide better insights into the relationship between different variables, empowering investors to make sound investment decisions.
By integrating these models into the pricing process, financial institutions can deliver accurate valuations for structured products, ensuring adequate compensation for the risks involved.
Credit Risk and Default Models
Credit risk and default models are essential tools in the valuation of structured products. These models evaluate the probability of a borrower defaulting on their payments and the potential losses that may arise as a consequence.
By assessing credit risk, firms can accurately determine the pricing of these products to account for the level of risk involved. One widely utilized credit risk model is the Credit Default Swap (CDS) model.
This model utilizes various factors such as the borrower’s credit rating, financial health, and market conditions to calculate the likelihood of default.
It enables investors to mitigate their risk by offering insurance against default. Another crucial model is the Default Probability Model, which estimates the probability of default based on historical data and financial ratios.
This model considers important factors such as leverage, liquidity, and profitability to evaluate the creditworthiness of the borrower.
Credit risk and default models play a significant role in ensuring the stability and profitability of structured products. Prior to investing in these products, investors must comprehend the potential risks involved.
By utilizing these models, financial institutions can accurately price structured products and make well-informed decisions based on their risk appetite and investment objectives.
It is important to acknowledge that credit risk and default models have limitations and uncertainties. Market volatility, economic conditions, and unforeseen events can affect the accuracy of these models.
Therefore, continuous monitoring and evaluation of the credit risk and default models are necessary to ensure their effectiveness in the pricing structured product.
Pricing Exotic Structured Products
When it comes to pricing exotic structured products, several factors come into play. These factors include the complexity of the product, the underlying assets involved, the market conditions, and the level of risk associated with the product.
Pricing Exotic Structured Products | The more complex the structured product is, the higher the price tends to be. Exotic structured products often involve unique features and customized components, which contribute to their higher pricing. |
Pricing Exotic Structured Products | The selection and performance of the underlying assets significantly impact the price of exotic structured products. Assets with higher volatility or unique characteristics can increase the complexity and risk, leading to a higher price. |
Pricing Exotic Structured Products | The current market conditions, such as interest rates, market volatility, and liquidity, play a vital role in determining the price of exotic structured products. These factors influence the expected returns and risks associated with the product. |
Pricing Exotic Structured Products | Exotic structured products generally involve a higher level of risk compared to traditional products. The pricing of these products incorporates the additional risk premium demanded by investors.
|
It’s important to note that pricing exotic structured products can be a complex process that requires sophisticated mathematical models and expertise. Financial institutions and pricing experts utilize various pricing techniques such as Monte Carlo simulations, copula models, and risk management strategies to accurately assess the value of these products.
Risk Management and Evaluation of Pricing Models
In the realm of the pricing structured product, the section we’re about to explore is all about risk management and evaluation of pricing models. Brace yourself for a journey into the depths of model validation and calibration, sensitivity analysis, stress testing, and crucial backtesting and performance evaluation.
We’ll uncover fascinating insights, backed by reliable sources, to help you navigate the intricate landscape of pricing models with confidence. Get ready to unravel the secrets that separate success from uncertainty in this exhilarating section.
Model Validation and Calibration
Model validation and calibration are essential aspects of the pricing structured product. They involve verifying and adjusting models to ensure they accurately reflect market conditions and provide reliable results.
Model Validation | Calibration |
Models used for the pricing structured product must undergo thorough validation to ensure their accuracy and reliability. | Calibration is the process of adjusting model parameters to align with market data. |
Validation helps identify any flaws or weaknesses in the model that may affect pricing and risk assessment. | Calibration ensures that the model produces results that align with observed market prices and other relevant data. |
It involves comparing model outputs with historical data, market prices, and other benchmarks. | Calibration typically involves using optimization techniques to find the best-fit model parameters. |
Validation also includes stress testing the model by evaluating its performance under extreme market conditions. | Calibration is an iterative process that may require continuous adjustments to ensure accurate pricing. |
Both model validation and calibration are crucial to ensure the accuracy of pricing models for structured products. By validating and calibrating models, financial institutions can have greater confidence in their pricing and risk management processes, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making.
Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity Analysis is an essential step in evaluating the pricing models for structured products. It helps to assess the impact of changes in input variables on the output or price of the products. By conducting a Sensitivity Analysis, financial analysts can gain insights into the sensitivity of the product’s price to different factors.
Factor | Impact | Observation |
Interest Rates | An increase in interest rates leads to a decrease in the price of fixed-income structured products. | For example, when interest rates rise by 1%, the price of a fixed-income structured product may decrease by 5%. |
Volatility | Higher volatility levels generally increase the price of options-based structured products. | A 10% increase in volatility may result in a 20% increase in the price of a structured product. |
Underlying Asset Price | Changes in the price of the underlying asset affect the value of structured products linked to it. | For instance, a 5% increase in the price of the underlying asset may lead to a 10% increase in the price of equity-linked structured products. |
Credit Rating | Downgrades in credit ratings can significantly impact the price of credit-linked structured products. | For every one-notch downgrade in credit rating, the price of credit-linked structured products may decrease by 3%. |
Sensitivity Analysis allows financial professionals to identify the factors that have the most significant impact on the pricing of structured products. By understanding the sensitivity of the products to various variables, they can make informed decisions and manage potential risks effectively.
Fact: Sensitivity Analysis is a crucial component of risk management as it helps to evaluate the potential impact of different factors on the pricing of structured products.
Stress Testing
Stress testing is a crucial process in assessing the resilience and stability of structured products. It involves simulating extreme scenarios to evaluate their impact.
When conducting stress tests, consider various scenarios such as market downturns, interest rate fluctuations, and credit rating downgrades.
- Scenario selection: Stress tests assess the impact on structured products by simulating extreme scenarios. It is essential to consider a range of stress scenarios, including market downturns, interest rate fluctuations, and credit rating downgrades.
- Quantitative analysis: Stress tests utilize quantitative analysis to measure potential losses and impacts on structured products. This involves evaluating changes in asset values, cash flows, and other relevant factors.
- Liquidity assessment: Stress testing evaluates the availability of liquidity during extreme scenarios. It ensures that structured products can withstand market stress without encountering liquidity issues.
- Risk measurement: Stress testing measures risks associated with structured products, such as market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk. Conducting stress tests helps identify potential vulnerabilities and weaknesses.
- Regulatory requirements: Regulatory authorities often impose stress testing requirements on financial institutions dealing with structured products. Compliance with these requirements is vital for ensuring financial stability and effective risk management.
Rigorous stress testing provides valuable insights for investors, issuers, and regulators. It helps identify potential risks and vulnerabilities, enabling informed decision-making and improved risk mitigation for structured products.
Backtesting and Performance Evaluation
The process of backtesting and performance evaluation is crucial when pricing structured products. By utilizing backtesting, we can analyze historical data and simulate the performance of the product under diverse market conditions to assess its effectiveness and potential risks.
Backtesting | Performance Evaluation |
Backtesting is the procedure of assessing a structured product’s performance using historical data. It provides valuable insights into the risk and return potential of the product by evaluating how it would have performed in the past. | Performance evaluation assists in determining how effectively the structured product has achieved its goals. It entails comparing the actual performance of the product with its expected performance, considering factors such as market conditions, underlying asset characteristics, and economic factors. |
Through backtesting, we can identify potential issues or weaknesses in the product design, enabling adjustments or improvements to be made. | Performance evaluation offers a comprehensive assessment of the product’s profitability, volatility, and risk-adjusted returns. |
Backtesting results can be utilized to refine pricing models and enhance the accuracy of future price estimations. | Performance evaluation assists in identifying strategies or areas that require adjustments to optimize the product’s performance. |
By incorporating backtesting and performance evaluation into the pricing process, financial institutions and investors can make more informed decisions, mitigate risks, and ensure the overall effectiveness of structured products.
When conducting backtesting and performance evaluation, it is important to:
- Use reliable historical data to ensure accurate analysis.
- Consider different market scenarios to capture a wide range of potential outcomes.
- Regularly review and update pricing models to reflect changing market conditions.
- Conduct sensitivity analysis to understand the impact of various factors on performance.
By following these guidelines, practitioners can enhance their understanding of structured products and make well-informed pricing decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
Structured products are pre-packaged investments that combine different financial instruments, such as a deposit or bonds and derivatives. They offer easy access to derivatives for retail investors and can replace traditional payment features with non-traditional payoffs.
The pricing of structured products depends on various factors, including interest rates, volatility, dividends, strike price, and the term of the product. Higher interest rates make capital-protected products more favorable, while volatility affects the cost of options embedded in the products. The strike price determines the level at which the product provides a positive return.
Investors in structured products should be aware of counterparty risk, which became important after the 2008 financial crisis. Liquidity is also a common risk associated with these products due to their customized nature. Additionally, there is issuer credit risk, lack of pricing transparency, and a potential loss of principal during a financial crisis.
Returns on structured products are paid at maturity and are contingent on the performance of underlying assets. They can offer a minimum return of the initial capital invested, plus a potential upside linked to an equity market. Investors can also customize structured products to trade off principal protection for more attractive performance potential, including leveraged upside participation or downside buffers.
Pricing strategies for structured products include cost-plus pricing, value-based pricing, and dynamic pricing. Cost-plus pricing considers the cost of production and adds a fixed percentage of profit. Value-based pricing sets prices based on customer willingness to pay. Dynamic pricing fluctuates based on market and customer demand.
Structured products offer derivative benefits to a range of investors, including retail investors and asset managers. They can provide customized risk-return objectives and complement traditional portfolios. These products were initially popular in Europe and later gained popularity in the United States as SEC-registered products accessible to retail investors.
Should I talk to a Financial Advisor When Buying a House?
In This Article Are you planning on purchasing your first home? Or thinking of splurging
Master Robert Kiyosaki: 10 Keys to Financial Freedom
In This Article Have you ever felt the earn, spend and save trilogy too mundane?

Can SIPs Make You Rich? Mutual Fund SIP Grow Your Wealth
In This Article Can SIPs make you rich? Systematic Investment Plans can help in wealth

Exclusive Investments of Elon Musk: Disruption, Vision, and Risk
In This Article A visionary entrepreneur who has been a consistent disruptor in the way


